
We’re thrilled to announce that the Kubeflow Trainer project has been integrated into the PyTorch ecosystem! This integration ensures that Kubeflow Trainer aligns with PyTorch’s standards and practices, giving developers a reliable, scalable, and community-backed solution to run PyTorch on Kubernetes.
To view the PyTorch Ecosystem, see the PyTorch Landscape. Learn more about how projects can join the PyTorch Ecosystem.
About Kubeflow Trainer
Kubeflow Trainer is a Kubernetes-native project enabling scalable, distributed training of AI models and purpose-built for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs). It simplifies the scale-out of training workloads on multiple nodes, managing large datasets efficiently and ensuring fault-tolerance.

The core features include:
- Simplify Kubernetes complexity: Kubeflow Trainer APIs are designed for two primary user personas – AI practitioners – ML engineers and data scientists who develop AI models using the Kubeflow Python SDK and TrainJob APIs, platform admins – administrators and DevOps engineers responsible for managing Kubernetes clusters and Kubeflow Trainer runtimes APIs. AI practitioners can focus on the application code in PyTorch without worrying about infrastructure details. Meanwhile, platform admins can flexibly schedule workload resources for maximum cluster utilization and cost efficiency. To support these roles, Kubeflow Trainer specifies purpose-built Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) that streamline model training and infrastructure management.
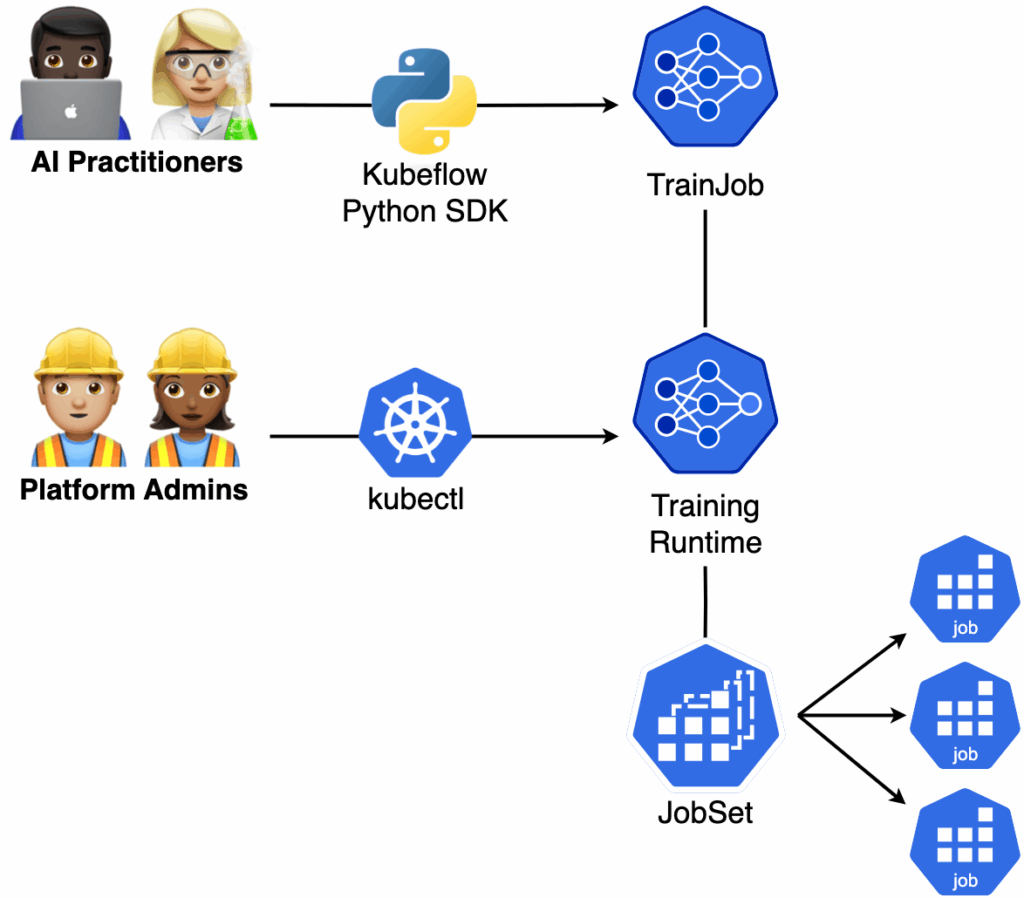
- Python SDK: A Pythonic interface designed for AI practitioners, abstract the details of interacting directly with Kubernetes APIs. It enables users to focus on developing PyTorch models without worrying about Kubernetes YAML configurations.
- Blueprints for LLMs fine-tuning on Kubernetes: With built-in trainers, Kubeflow Trainer enables AI practitioners to seamlessly fine-tune their favorite LLMs using the desired configuration for datasets, LoRA parameters, learning rate, etc. In the first release, it implements recipes to support various fine-tuning strategies, including Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), Knowledge Distillation, DPO, PPO, GRPO, and Quantization-Aware Training. Community is working towards adding more builtin trainers powered by LLaMA-Factory, Unsloth, HuggingFace TRL to enable efficient LLMs fine-tuning.
- Optimized GPU utilization: Kubeflow Trainer maximizes GPU efficiency by streaming large-scale data directly to distributed GPUs using an in-memory distributed data cache powered by Apache Arrow and Apache DataFusion
- Advanced scheduling capabilities: Kubeflow Trainer supports gang scheduling through the PodGroupPolicy API, enabling coordinated scheduling of pods across nodes. It also integrates with Kubernetes schedulers such as Kueue, Coscheduling, Volcano, and KAI Scheduler to ensure all required resources are allocated before training jobs start.
- Accelerate MPI workloads on Kubernetes: Kubeflow Trainer supports MPI-based runtimes such as DeepSpeed and MLX. It handles all necessary orchestration of MPI workloads with SSH-based optimization to boost MPI performance.
- Improved resilience and fault-tolerance: By leveraging Kubernetes-native APIs like Jobs and JobSets, Kubeflow Trainer improves reliability and efficiency of AI workloads. With support for the PodFailurePolicy API, users can reduce cost by avoiding unnecessary restarts. Additionally, the SuccessPolicy API allows training jobs to complete early once the target objective is achieved.
Background and Evolution
This project was originally started as a distributed training operator for TensorFlow (e.g. TFJob), and later we merged efforts from other Kubeflow Training Operators (e.g. PyTorchJob, MPIJob) to provide a unified and simplified experience for both users and developers. We are very grateful to all who filed issues or helped resolve them, asked and answered questions, and were part of inspiring discussions. We’d also like to thank everyone who’s contributed to and maintained the original operators.
By joining the PyTorch Ecosystem, we strive to apply best practices of deploying distributed PyTorch applications on Kubernetes and bring first-class PyTorch support in Kubeflow Trainer.
Integrations with PyTorch Ecosystem
Kubeflow Trainer is deeply integrated with the PyTorch ecosystem, supporting a broad range of tools and libraries—including torch, DeepSpeed, HuggingFace, Horovod, and more.
It empowers PyTorch users to implement advanced distributed training strategies such as Distributed Data Parallel (DDP), Fully Sharded Data Parallel (FSDP & FSDP2), and Tensor Parallelism, enabling efficient large-scale model training on Kubernetes.
Additionally, Kubeflow Trainer supports data parallelism using PyTorch IterableDatasets, streaming data directly from distributed in-memory data cache nodes. This allows scalable training even with massive datasets that exceed local memory capacity.
Quick Start
Follow the steps below to quickly deploy Kubeflow Trainer and run your first training job.
Prerequisites
Install Kubeflow Trainer
Deploy Kubeflow Trainer control plane on your local kind cluster:
$ kind create cluster
$ kubectl apply --server-side -k "https://github.com/kubeflow/trainer.git/manifests/overlays/manager?ref=v2.0.0"
# Ensure that JobSet and Trainer controller manager are running.
$ kubectl get pods -n kubeflow-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
jobset-controller-manager-54968bd57b-88dk4 2/2 Running 0 65s
kubeflow-trainer-controller-manager-cc6468559-dblnw 1/1 Running 0 65s
# Deploy the Kubeflow Trainer runtimes.
$ kubectl apply --server-side -k "https://github.com/kubeflow/trainer.git/manifests/overlays/runtimes?ref=v2.0.0"
# Install Kubeflow SDK
$ pip install git+https://github.com/kubeflow/sdk.git@64d74db2b6c9a0854e39450d8d1c0201e1e9b3f7#subdirectory=pythonDefine PyTorch Training Function
After installing the Kubeflow Trainer, define your PyTorch training function that contains end-to-end training script:
def train_pytorch():
import os
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, DistributedSampler
from torchvision import datasets, transforms, models
# [1] Configure CPU/GPU device and distributed backend.
device, backend = ("cuda", "nccl") if torch.cuda.is_available() else ("cpu", "gloo")
dist.init_process_group(backend=backend)
local_rank = int(os.getenv("LOCAL_RANK", 0))
device = torch.device(f"{device}:{local_rank}")
# [2] Get the pre-defined model.
model = models.shufflenet_v2_x0_5(num_classes=10)
model.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 24, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model.to(device))
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9)
# [3] Get the FashionMNIST dataset and distribute it across all available devices.
if local_rank == 0: # Download dataset only on local_rank=0 process.
dataset = datasets.FashionMNIST("./data", train=True, download=True, transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()]))
dist.barrier()
dataset = datasets.FashionMNIST("./data", train=True, download=False, transform=transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()]))
train_loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=100, sampler=DistributedSampler(dataset))
# [4] Define the PyTorch training loop.
for epoch in range(3):
for batch_idx, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device)
# Forward and Backward pass
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = torch.nn.functional.cross_entropy(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % 10 == 0 and dist.get_rank() == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch} [{batch_idx * len(inputs)}/{len(train_loader.dataset)}] "
f"Loss: {loss.item():.4f}"
)
Run PyTorch on Kubernetes with TrainJob
After defining the training function, use the Kubeflow SDK to create TrainJob:
from kubeflow.trainer import TrainerClient, CustomTrainer
job_id = TrainerClient().train(
trainer=CustomTrainer(
func=train_pytorch,
num_nodes=2,
resources_per_node={
"cpu": 3,
"memory": "3Gi",
# "gpu": 2, # Uncomment this line if you have GPUs.
},
),
runtime=TrainerClient().get_runtime("torch-distributed"),
)
Get the TrainJob Results
After creating the TrainJob, you should be able to list it:
for job in TrainerClient().list_jobs():
print(f"TrainJob: {job.name}, Status: {job.status}")
TrainJob: q33a18f65635, Status: Created It may take a few minutes for the TrainJob to pull the PyTorch image the first time. Once the image is pulled, the TrainJob‘s steps should transition to Running status. Each step represents a training node, and the number of devices per step corresponds to the number of devices on that node.
for s in TrainerClient().get_job(name=job_id).steps:
print(f"Step: {s.name}, Status: {s.status}, Devices: {s.device} x {s.device_count}")
Step: node-0, Status: Running, Devices: cpu x 3
Step: node-1, Status: Running, Devices: cpu x 3 After steps are running, you can check the TrainJob logs. The dataset of 60,000 samples has been evenly distributed across 6 CPUs, with each device processing 10,000 samples: 60,000 / 6 = 10,000
print(TrainerClient().get_job_logs(name=job_id)["node-0"])
...
Epoch 0 [8000/60000] Loss: 0.4476
Epoch 0 [9000/60000] Loss: 0.4784
Epoch 1 [0/60000] Loss: 0.3909
Epoch 1 [1000/60000] Loss: 0.4888
Epoch 1 [2000/60000] Loss: 0.4100
... Congratulations, you created your first distributed training job with PyTorch and Kubeflow Trainer!
What’s next
Kubeflow Trainer has exciting roadmap including the following items:
- Local TrainJob Execution – run Kubeflow Trainer jobs locally without Kubernetes.
- Distributed Data Cache – stream in-memory distributed data powered by Apache Arrow and Apache DataFusion.
- Advanced scheduling capabilities – improve resources management and gang-scheduling capabilities by integrating with Kueue, KAI Scheduler, Volcano.
- Support for JAX runtime.
- Automate Checkpointing for GPU-accelerated workloads.
Call to Action
We are excited to welcome Kubeflow Trainer to the PyTorch ecosystem! Kubeflow Trainer democratizes AI model training on Kubernetes and significantly improves the development experience for AI practitioners. We invite you to explore the following resources to learn more about the project:
- Read the Kubeflow Trainer v2 announcement blog post and release notes.
- Explore the official Kubeflow Trainer documentation.
- Join the conversations in the #kubeflow-trainer Slack channel.
- Attend our bi-weekly Kubeflow Trainer community calls every Wednesday.
- Share your use cases or feature proposals by opening an issue on the GitHub repository.
- Tell your store by writing a Kubeflow blog post or speaking at upcoming Kubeflow Events.
- Explore the Kubeflow Python SDK for AI practitioners.
We can’t wait to see what you’ll build with Kubeflow Trainer!
