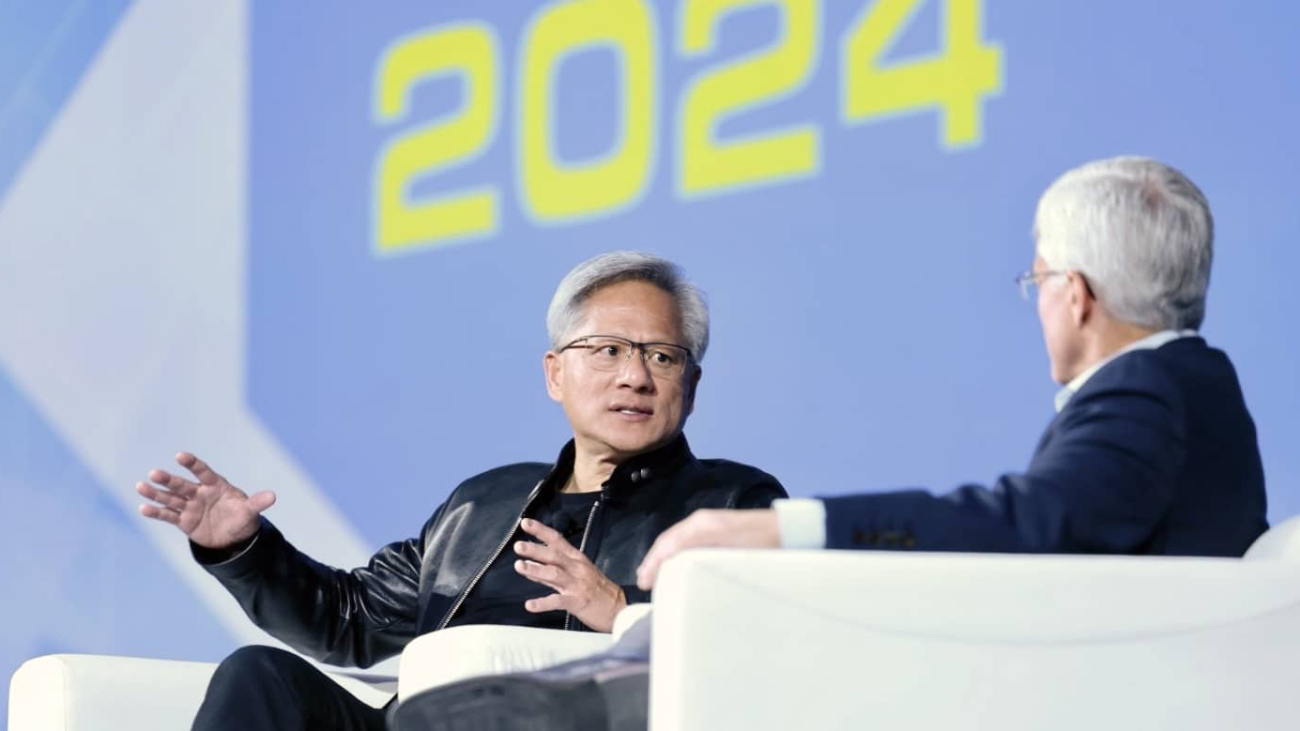
The electric grid and the utilities managing it have an important role to play in the next industrial revolution that’s being driven by AI and accelerated computing, said NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang Monday at the annual meeting of the Edison Electric Institute (EEI), an association of U.S. and international utilities.
“The future of digital intelligence is quite bright, and so the future of the energy sector is bright, too,” said Huang in a keynote before an audience of more than a thousand utility and energy industry executives.
Like other companies, utilities will apply AI to increase employee productivity, but “the greatest impact and return is in applying AI in the delivery of energy over the grid,” said Huang, in conversation with Pedro Pizarro, the chair of EEI and president and CEO of Edison International, the parent company of Southern California Edison, one of the nation’s largest electric utilities.
For example, Huang described how grids will use AI-powered smart meters to let customers sell their excess electricity to neighbors.
“You will connect resources and users, just like Google, so your power grid becomes a smart network with a digital layer like an app store for energy,” he said.
“My sense is, like previous industrial revolutions, [AI] will drive productivity to levels that we’ve never seen,” he added.
A video of the fireside chat will be available here soon.
AI Lights Up Electric Grids
Today, electric grids are mainly one-way systems that link a few big power plants to many users. They’ll increasingly become two-way, flexible and distributed networks with solar and wind farms connecting homes and buildings that sport solar panels, batteries and electric vehicle chargers.
It’s a big job that requires autonomous control systems that process and analyze in real time a massive amount of data — work well suited to AI and accelerated computing.
AI is being applied to use cases across electric grids, thanks to a wide ecosystem of companies using NVIDIA’s technologies.
In a recent GTC session, utility vendor Hubbell and startup Utilidata, a member of the NVIDIA Inception program, described a new generation of smart meters using the NVIDIA Jetson platform that utilities will deploy to process and analyze real-time grid data using AI models at the edge. Deloitte announced today its support for the effort.
Siemens Energy detailed in a separate GTC session its work with AI and NVIDIA Omniverse creating digital twins of transformers in substations to improve predictive maintenance, boosting grid resilience. And a video reports on how Siemens Gamesa used Omniverse and accelerated computing to optimize turbine placements for a large wind farm.
“Deploying AI and advanced computing technologies developed by NVIDIA enables faster and better grid modernization and we, in turn, can deliver for our customers,” said Maria Pope, CEO of Portland General Electric in Oregon.
NVIDIA Delivers 45,000x Gain in Energy Efficiency
The advances come as NVIDIA drives down the costs and energy needed to deploy AI.
Over the last eight years, NVIDIA increased energy efficiency of running AI inference on state-of-the-art large language models a whopping 45,000x, Huang said in his recent keynote at COMPUTEX.
NVIDIA Blackwell architecture GPUs will provide 20x greater energy efficiency than CPUs for AI and high-performance computing. If all CPU servers for these jobs transitioned to GPUs, users would save 37 terawatt-hours a year, the equivalent of 25 million metric tons of carbon dioxide and the electricity use of 5 million homes.
That’s why NVIDIA-powered systems swept the top six spots and took seven of the top 10 in the latest ranking of the Green500, a list of the world’s most energy-efficient supercomputers.
In addition, a recent report calls for governments to accelerate adoption of AI as a significant new tool to drive energy efficiency across many industries. It cited examples of utilities adopting AI to make the electric grid more efficient.
Learn more about how utilities are deploying AI and accelerated computing to improve operations, saving cost and energy.














 NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)
NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN) 
