The last decade of the Industry 4.0 revolution has shown the value and importance of machine learning (ML) across verticals and environments, with more impact on manufacturing than possibly any other application. Organizations implementing a more automated, reliable, and cost-effective Operational Technology (OT) strategy have led the way, recognizing the benefits of ML in predicting assembly line failures to avoid costly and unplanned downtime. Still, challenges remain for teams of all sizes to quickly, and with little effort, demonstrate the value of ML-based anomaly detection in order to persuade management and finance owners to allocate the budget required to implement these new technologies. Without access to data scientists for model training, or ML specialists to deploy solutions at the local level, adoption has seemed out of reach for teams on the factory floor.
Now, teams that collect sensor data signals from machines in the factory can unlock the power of services like Amazon Timestream, Amazon Lookout for Equipment, and AWS IoT Core to easily spin up and test a fully production-ready system at the local edge to help avoid catastrophic downtime events. Lookout for Equipment uses your unique ML model to analyze incoming sensor data in real time and accurately identify early warning signs that could lead to machine failures. This means you can detect equipment abnormalities with speed and precision, quickly diagnose issues, take action to reduce expensive downtime, and reduce false alerts. Response teams can be alerted with specific pinpoints to which sensors are indicating the issue, and the magnitude of impact on the detected event.
In this post, we show you how you can set up a system to simulate events on your factory floor with a trained model and detect abnormal behavior using Timestream, Lookout for Equipment, and AWS Lambda functions. The steps in this post emphasize the AWS Management Console UI, showing how technical people without a developer background or strong coding skills can build a prototype. Using simulated sensor signals will allow you to test your system and gain confidence before cutting over to production. Lastly, in this example, we use Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) to show how teams can receive notifications of predicted events and respond to avoid catastrophic effects of assembly line failures. Additionally, teams can use Amazon QuickSight for further analysis and dashboards for reporting.
Solution overview
To get started, we first collect a historical dataset from your factory sensor readings, ingest the data, and train the model. With the trained model, we then set up IoT Device Simulator to publish MQTT signals to a topic that will allow testing of the system to identify desired production settings before production data is used, keeping costs low.
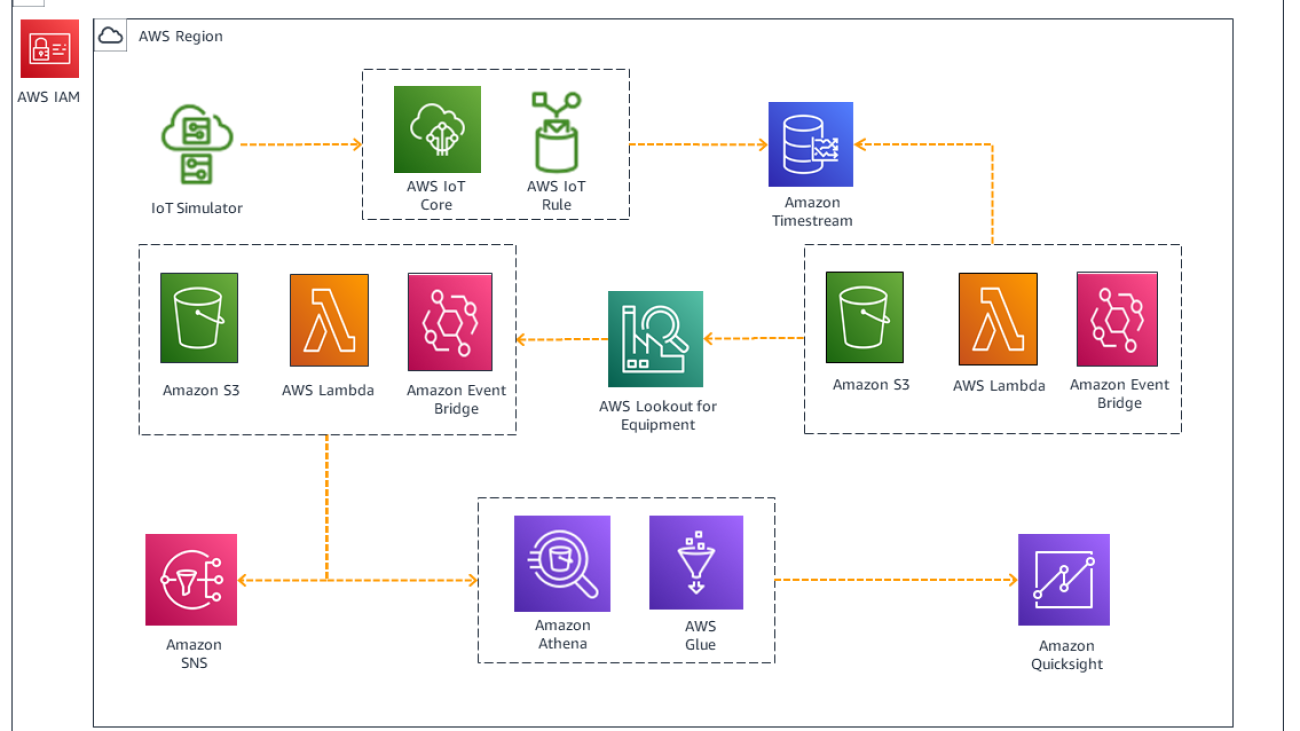
The following diagram illustrates our solution architecture.

The workflow contains the following steps:
- Use sample data to train the Lookout for Equipment model, and the provided labeled data to improve model accuracy. With a sample rate of 5 minutes, we can train the model in 20–30 minutes.
- Run an AWS CloudFormation template to enable IoT Simulator, and create a simulation to publish an MQTT topic in the format of the sensor data signals.
- Create an IoT rule action to read the MQTT topic an send the topic payload to Timestream for storage. These are the real-time datasets that will be used for inferencing with the ML model.
- Set up a Lambda function triggered by Amazon EventBridge to convert data into CSV format for Lookout for Equipment.
- Create a Lambda function to parse Lookout for Equipment model inferencing output file in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) and, if failure is predicted, send an email to the configured address. Additionally, use AWS Glue, Amazon Athena, and QuickSight to visualize the sensor data contributions to the predicted failure event.
Prerequisites
You need access to an AWS account to set up the environment for anomaly detection.
Simulate data and ingest it into the AWS Cloud
To set up your data and ingestion configuration, complete the following steps:
- Download the training file subsystem-08_multisensor_training.csv and the labels file labels_data.csv. Save the files locally.
- On the Amazon S3 console in your preferred Region, create a bucket with a unique name (for example,
l4e-training-data), using the default configuration options. - Open the bucket and choose Upload, then Add files.

- Upload the training data to a folder called
/training-dataand the label data to a folder called/labels.
Next, you create the ML model to be trained with the data from the S3 bucket. To do this, you first need to create a project.
- On the Lookout for Equipment console, choose Create project.

- Name the project and choose Create project.
- On the Add dataset page, specify your S3 bucket location.
- Use the defaults for Create a new role and Enable CloudWatch Logs.
- Choose By filename for Schema detection method.
- Choose Start ingestion.
Ingestion takes a few minutes to complete.
- When ingestion is complete, you can review the details of the dataset by choosing View Dataset.
- Scroll down the page and review the Details by sensor section.
- Scroll to the bottom of the page to see that the sensor grade for data from three of the sensors is labeled
Low. - Select all the sensor records except the three with Low grade.
- Choose Create model.

- On the Specify model details page, give the model a name and choose Next.
- On the Configure input data page, enter values for the training and evaluation settings and a sample rate (for this post, 1 minute).
- Skip the Off-time detection settings and choose Next.

- On the Provide data labels page, specify the S3 folder location where the label data is.
- Select Create a new role.
- Choose Next.

- On the Review and train page, choose Start training.
With a sample rate of 5 minutes, the model should take 20–30 minutes to build.
While the model is building, we can set up the rest of the architecture.
Simulate sensor data
- Choose Launch Stack to launch a CloudFormation template to set up the simulated sensor signals using IoT Simulator.
- After the template has launched, navigate to the CloudFormation console.
- On the Stacks page, choose
IoTDeviceSimulatorto see the stack details. - On the Outputs tab, find the
ConsoleURLkey and the corresponding URL value.
- Choose the URL to open the IoT Device Simulator login page.
- Create a user name and password and choose SIGN IN.
- Save your credentials in case you need to sign in again later.

- From the IoT Device Simulator menu bar, choose Device Types.
- Enter a device type name, such as
My_testing_device. - Enter an MQTT topic, such as
factory/line/station/simulated_testing. - Choose Add attribute.

- Enter the values for the attribute
signal5, as shown in the following screenshot. - Choose Save.

- Choose Add attribute again and add the remaining attributes to match the sample signal data, as shown in the following table.
| . | signal5 | signal6 | signal7 | signal8 | signal48 | signal49 | signal78 | signal109 | signal120 | signal121 |
| Low | 95 | 347 | 27 | 139 | 458 | 495 | 675 | 632 | 742 | 675 |
| Hi | 150 | 460 | 217 | 252 | 522 | 613 | 812 | 693 | 799 | 680 |
- On the Simulations tab, choose Add Simulation.
- Give the simulation a name.
- Specify Simulation type as User created, Device type as the recently created device, Data transmission interval as 60, and Data transmission duration as 3600.
- Finally, start the simulation you just created and see the payloads generated on the Simulation Details page by choosing View.
Now that signals are being generated, we can set up IoT Core to read the MQTT topics and direct the payloads to the Timestream database.
- On the IoT Core console, under Message Routing in the navigation pane, choose Rules.
- Choose Create rule.
- Enter a rule name and choose Next.
- Enter the following SQL statement to pull all the values from the published MQTT topic:

- Choose Next.
- For Rule actions, search for the Timestream table.
- Choose Create Timestream database.
A new tab opens with the Timestream console.
- Select Standard database.
- Name the database
sampleDBand choose Create database.

You’re redirected to the Timestream console, where you can view the database you created.
- Return to the IoT Core tab and choose
sampleDBfor Database name. - Choose Create Timestream table to add a table to the database where the sensor data signals will be stored.
- On the Timestream console Create table tab, choose
sampleDBfor Database name, entersignalTablefor Table name, and choose Create table. - Return to the IoT Core console tab to complete the IoT message routing rule.
- Enter
Simulated_signalfor Dimensions name and 1 for Dimensions value, then choose Create new role.

- Name the role
TimestreamRoleand choose Next. - On the Review and create page, choose Create.
You have now added a rule action in IoT Core that directs the data published to the MQTT topic to a Timestream database.
Query Timestream for analysis
To query Timestream for analysis, complete the following steps:
- Validate the data is being stored in the database by navigating to the Timestream console and choosing Query Editor.
- Choose Select table, then choose the options menu and Preview data.
- Choose Run to query the table.

Now that data is being stored in the stream, you can use Lambda and EventBridge to pull data every 5 minutes from the table, format it, and send it to Lookout for Equipment for inference and prediction results.
- On the Lambda console, choose Create function.
- For Runtime, choose Python 3.9.
- For Layer source, select Specify an ARN.
- Enter the correct ARN for your Region from the aws pandas resource.
- Choose Add.

- Enter the following code into the function and edit it to match the S3 path to a bucket with the folder
/input(create a bucket folder for these data stream files if not already present).
This code uses the awswrangler library to easily format the data in the required CSV form needed for Lookout for Equipment. The Lambda function also dynamically names the data files as required.
- Choose Deploy.
- On the Configuration tab, choose General configuration.
- For Timeout, choose 5 minutes.
- In the Function overview section, choose Add trigger with EventBridge as the source.
- Select Create a new rule.
- Name the rule
eventbridge-cron-job-lambda-read-timestreamand addrate(5 minutes)for Schedule expression. - Choose Add.

- Add the following policy to your Lambda execution role:
Predict anomalies and notify users
To set up anomaly prediction and notification, complete the following steps:
- Return to the Lookout for Equipment project page and choose Schedule inference.
- Name the schedule and specify the model created previously.
- For Input data, specify the S3
/inputlocation where files are written using the Lambda function and EventBridge trigger. - Set Data upload frequency to 5 minutes and leave Offset delay time at 0 minutes.
- Set an S3 path with
/outputas the folder and leave other default values. - Choose Schedule inference.
After 5 minutes, check the S3 /output path to verify prediction files are created. For more information about the results, refer to Reviewing inference results.
Finally, you create a second Lambda function that triggers a notification using Amazon SNS when an anomaly is predicted.
- On the Amazon SNS console, choose Create topic.
- For Name, enter
emailnoti. - Choose Create.
- In the Details section, for Type, select Standard.
- Choose Create topic.

- On the Subscriptions tab, create a subscription with Email type as Protocol and an endpoint email address you can access.
- Choose Create subscription and confirm the subscription when the email arrives.
- On the Topic tab, copy the ARN.

- Create another Lambda function with the following code and enter the ARN topic in
MY_SYS_ARN: - Choose Deploy to deploy the function.
When Lookout for Equipment detects an anomaly, the prediction value is 1 in the results. The Lambda code uses the JSONL file and sends an email notification to the address configured.
- Under Configuration, choose Permissions and Role name.
- Choose Attach policies and add
AmazonS3FullAccessandAmazonSNSFullAccessto the role. - Finally, add an S3 trigger to the function and specify the
/outputbucket.

After a few minutes, you will start to see emails arrive every 5 minutes.
Visualize inference results
After Amazon S3 stores the prediction results, we can use the AWS Glue Data Catalog with Athena and QuickSight to create reporting dashboards.
- On the AWS Glue console, choose Crawlers in the navigation pane.
- Choose Create crawler.
- Give the crawler a name, such as
inference_crawler. - Choose Add a data source and select the S3 bucket path with the
results.jsonlfiles. - Select Crawl all sub-folders.
- Choose Add an S3 data source.
- Choose Create new IAM role.
- Create a database and provide a name (for example,
anycompanyinferenceresult). - For Crawler schedule, choose On demand.
- Choose Next, then choose Create crawler.
- When the crawler is complete, choose Run crawler.

- On the Athena console, open the query editor.
- Choose Edit settings to set up a query result location in Amazon S3.
- If you don’t have a bucket created, create one now via the Amazon S3 console.
- Return to the Athena console, choose the bucket, and choose Save.
- Return to the Editor tab in the query editor and run a query to
select *from the/outputS3 folder. - Review the results showing anomaly detection as expected.

- To visualize the prediction results, navigate to the QuickSight console.
- Choose New analysis and New dataset.
- For Dataset source, choose Athena.
- For Data source name, enter
MyDataset. - Choose Create data source.
- Choose the table you created, then choose Use custom SQL.

- Enter the following query:
- Confirm the query and choose Visualize.
- Choose Pivot table.
- Specify timestamp and sensor for Rows.
- Specify prediction and ScoreValue for Values.

- Choose Add Visual to add a visual object.
- Choose Vertical bar chart.
- Specify Timestamp for X axis, ScoreValue for Value, and Sensor for Group/Color.
- Change ScoreValue to Aggregate:Average.

Clean up
Failure to delete resources can result in additional charges. To clean up your resources, complete the following steps:
- On the QuickSight console, choose Recent in the navigation pane.
- Delete all the resources you created as part of this post.
- Navigate to the Datasets page and delete the datasets you created.
- On the Lookout for Equipment console, delete the projects, datasets, models, and inference schedules used in this post.
- On the Timestream console, delete the database and associated tables.
- On the Lambda console, delete the EventBridge and Amazon S3 triggers.
- Delete the S3 buckets, IoT Core rule, and IoT simulations and devices.
Conclusion
In this post, you learned how to implement machine learning for predictive maintenance using real-time streaming data with a low-code approach. You learned different tools that can help you in this process, using managed AWS services like Timestream, Lookout for Equipment, and Lambda, so operational teams see the value without adding additional workloads for overhead. Because the architecture uses serverless technology, it can scale up and down to meet your needs.
For more data-based learning resources, visit the AWS Blog home page.
About the author
 Matt Reed is a Senior Solutions Architect in Automotive and Manufacturing at AWS. He is passionate about helping customers solve problems with cool technology to make everyone’s life better. Matt loves to mountain bike, ski, and hang out with friends, family, and dogs and cats.
Matt Reed is a Senior Solutions Architect in Automotive and Manufacturing at AWS. He is passionate about helping customers solve problems with cool technology to make everyone’s life better. Matt loves to mountain bike, ski, and hang out with friends, family, and dogs and cats.


 Martin Schade is a Senior ML Product SA with the Amazon Textract team. He has 20+ years of experience with internet-related technologies, engineering and architecting solutions and joined AWS in 2014, first guiding some of the largest AWS customers on most efficient and scalable use of AWS services and later focused on AI/ML with a focus on computer vision and at the moment is obsessed with extracting information from documents.
Martin Schade is a Senior ML Product SA with the Amazon Textract team. He has 20+ years of experience with internet-related technologies, engineering and architecting solutions and joined AWS in 2014, first guiding some of the largest AWS customers on most efficient and scalable use of AWS services and later focused on AI/ML with a focus on computer vision and at the moment is obsessed with extracting information from documents.




 Alex Emilcar is a Senior Solutions Architect in the Amazon Machine Learning Solutions Lab, where he helps customers build digital experiences with AWS AI technologies. Alex has over 10 years of technology experience working in different capacities from developer, infrastructure engineer, and Solutions Architecture. In his spare time, Alex likes to spend time reading and doing yard work.
Alex Emilcar is a Senior Solutions Architect in the Amazon Machine Learning Solutions Lab, where he helps customers build digital experiences with AWS AI technologies. Alex has over 10 years of technology experience working in different capacities from developer, infrastructure engineer, and Solutions Architecture. In his spare time, Alex likes to spend time reading and doing yard work.