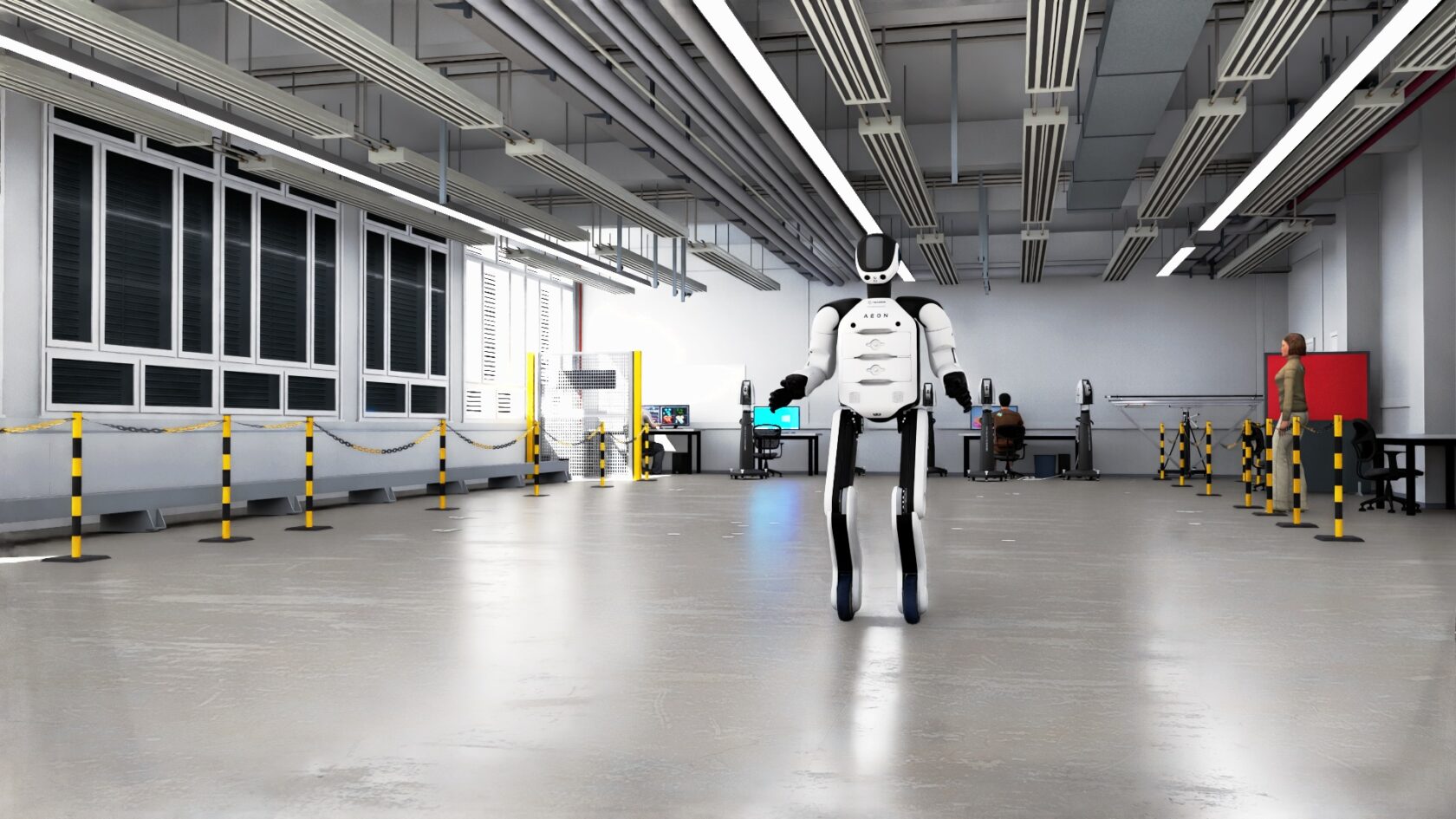
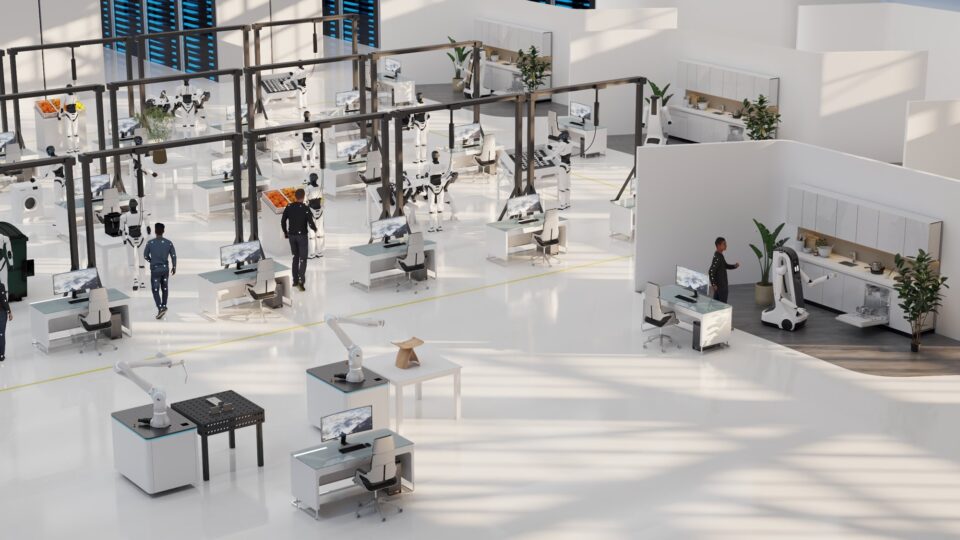
From the heart of Germany’s automotive sector to manufacturing hubs across France and Italy, Europe is embracing industrial AI and advanced AI-powered robotics to address labor shortages, boost productivity and fuel sustainable economic growth.
Robotics companies are developing humanoid robots and collaborative systems that integrate AI into real-world manufacturing applications. Supported by a $200 billion investment initiative and coordinated efforts from the European Commission, Europe is positioning itself at the forefront of the next wave of industrial automation, powered by AI.
This momentum is on full display at Automatica — Europe’s premier conference on advancements in robotics, machine vision and intelligent manufacturing — taking place this week in Munich, Germany.
NVIDIA and its ecosystem of partners and customers are showcasing next-generation robots, automation and AI technologies designed to accelerate the continent’s leadership in smart manufacturing and logistics.
NVIDIA Technologies Boost Robotics Development
Central to advancing robotics development is Europe’s first industrial AI cloud, announced at NVIDIA GTC Paris at VivaTech earlier this month. The Germany-based AI factory, featuring 10,000 NVIDIA GPUs, provides European manufacturers with secure, sovereign and centralized AI infrastructure for industrial workloads. It will support applications ranging from design and engineering to factory digital twins and robotics.
To help accelerate humanoid development, NVIDIA released NVIDIA Isaac GR00T N1.5 — an open foundation model for humanoid robot reasoning and skills. This update enhances the model’s adaptability and ability to follow instructions, significantly improving its performance in material handling and manufacturing tasks.
To help post-train GR00T N1.5, NVIDIA has also released the Isaac GR00T-Dreams blueprint — a reference workflow for generating vast amounts of synthetic trajectory data from a small number of human demonstrations — enabling robots to generalize across behaviors and adapt to new environments with minimal human demonstration data.
In addition, early developer previews of NVIDIA Isaac Sim 5.0 and Isaac Lab 2.2 — open-source robot simulation and learning frameworks optimized for NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000 workstations — are now available on GitHub.
Robotics Leaders Tap NVIDIA Simulation Technology to Develop and Deploy Humanoids and More
Robotics developers and solutions providers across the globe are integrating NVIDIA’s three computers to train, simulate and deploy robots.
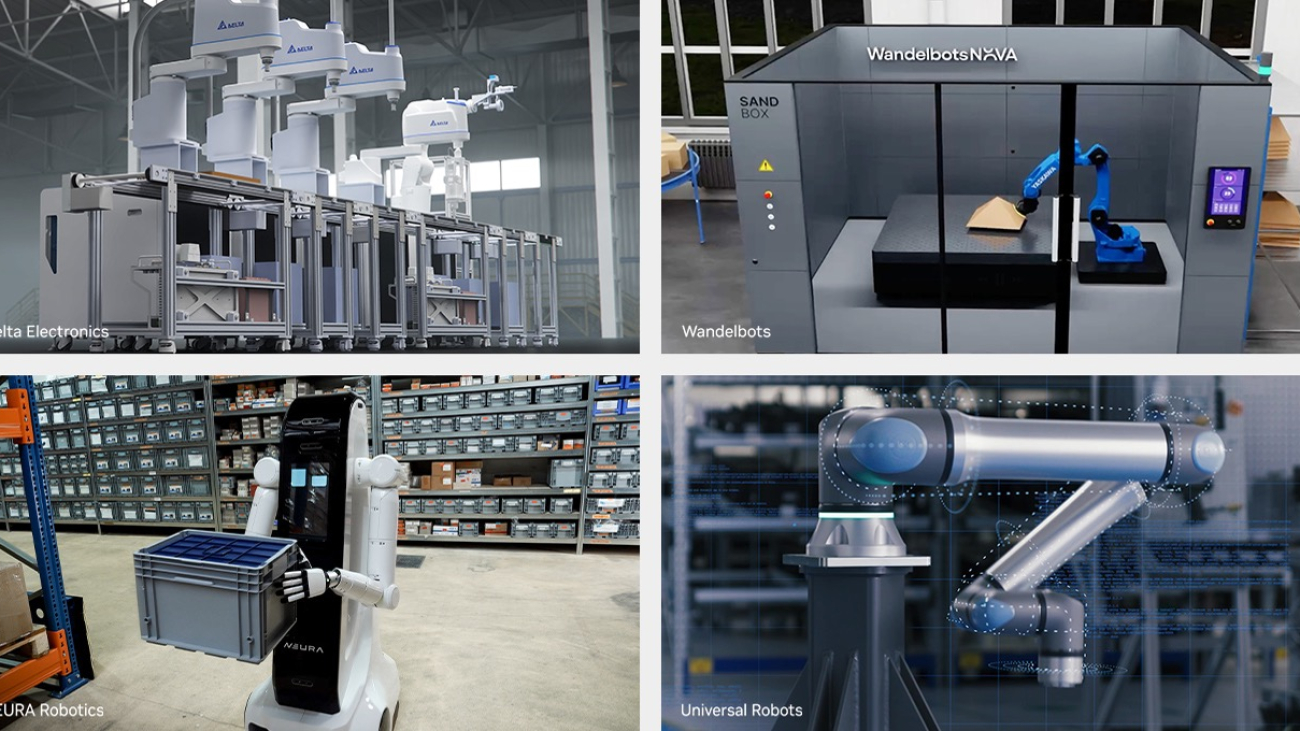
NEURA Robotics, a German robotics company and pioneer for cognitive robots, unveiled the third generation of its humanoid, 4NE1, designed to assist humans in domestic and professional environments through advanced cognitive capabilities and humanlike interaction. 4NE1 is powered by GR00T N1 and was trained in Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab before real-world deployment.
NEURA Robotics is also presenting Neuraverse, a digital twin and interconnected ecosystem for robot training, skills and applications, fully compatible with NVIDIA Omniverse technologies.
Delta Electronics, a global leader in power management and smart green solutions, is debuting two next-generation collaborative robots: D-Bot Mar and D-Bot 2 in 1 — both trained using Omniverse and Isaac Sim technologies and libraries. These cobots are engineered to transform intralogistics and optimize production flows.
Wandelbots, the creator of the Wandelbots NOVA software platform for industrial robotics, is partnering with SoftServe, a global IT consulting and digital services provider, to scale simulation-first automating using NVIDIA Isaac Sim, enabling virtual validation and real-world deployment with maximum impact.
Cyngyn, a pioneer in autonomous mobile robotics, is integrating its DriveMod technology into Isaac Sim to enable large-scale, high fidelity virtual testing of advanced autonomous operation. Purpose-built for industrial applications, DriveMod is already deployed on vehicles such as the Motrec MT-160 Tugger and BYD Forklift, delivering sophisticated automation to material handling operations.
Doosan Robotics, a company specializing in AI robotic solutions, will showcase its “sim to real” solution, using NVIDIA Isaac Sim and cuRobo. Doosan will be showcasing how to seamlessly transfer tasks from simulation to real robots across a wide range of applications — from manufacturing to service industries.
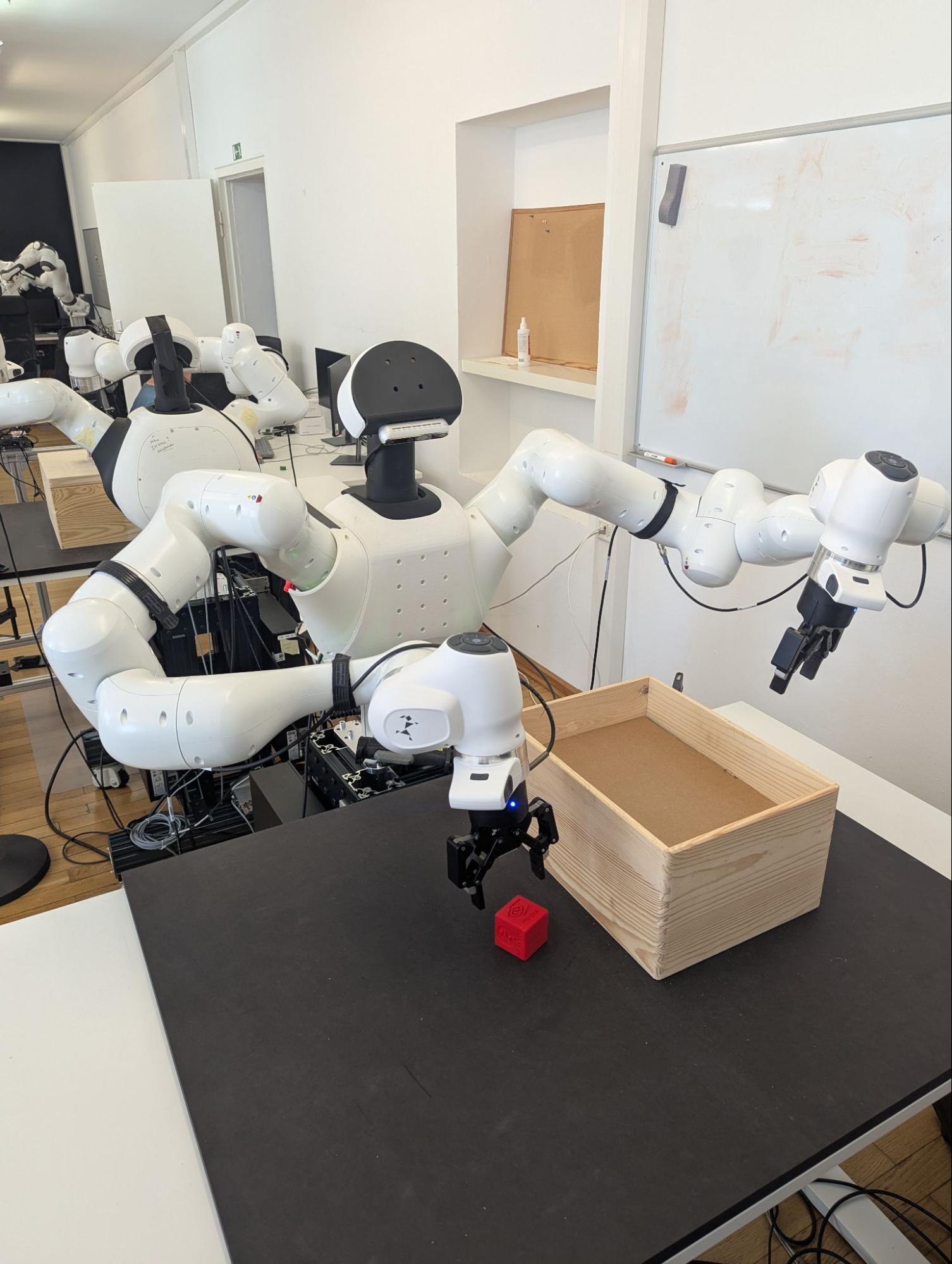
Franka Robotics has integrated Isaac GR00T N1.5 into a dual-arm Franka Research 3 (FR3) robot for robotic control. The integration of GR00T N1.5 allows the system to interpret visual input, understand task context and autonomously perform complex manipulation — without the need for task-specific programming or hardcoded logic.

Hexagon, the global leader in measurement technologies, launched its new humanoid, dubbed AEON. With its unique locomotion system and multimodal sensor fusion, and powered by NVIDIA’s three-computer solution, AEON is engineered to perform a wide range of industrial applications, from manipulation and asset inspection to reality capture and operator support.
Intrinsic, a software and AI robotics company, is integrating Intrinsic Flowstate with Omniverse and OpenUSD for advanced visualization and digital twins that can be used in many industrial use cases. The company is also using NVIDIA foundation models to enhance robot capabilities like grasp planning through AI and simulation technologies.
SCHUNK, a global leader in gripping systems and automation technology, is showcasing its innovative grasping kit powered by the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin module. The kit intelligently detects objects and calculates optimal grasping points. Schunk is also demonstrating seamless simulation-to-reality transfer using IGS Virtuous software — built on Omniverse technologies — to control a real robot through simulation in a pick-and-place scenario.
Universal Robots is showcasing UR15, its fastest cobot yet. Powered by the UR AI Accelerator — developed with NVIDIA and running on Jetson AGX Orin using CUDA-accelerated Isaac libraries — UR15 helps set a new standard for industrial automation.
Vention, a full-stack software and hardware automation company, launched its Machine Motion AI, built on CUDA-accelerated Isaac libraries and powered by Jetson. Vention is also expanding its lineup of robotic offerings by adding the FR3 robot from Franka Robotics to its ecosystem, enhancing its solutions for academic and research applications.
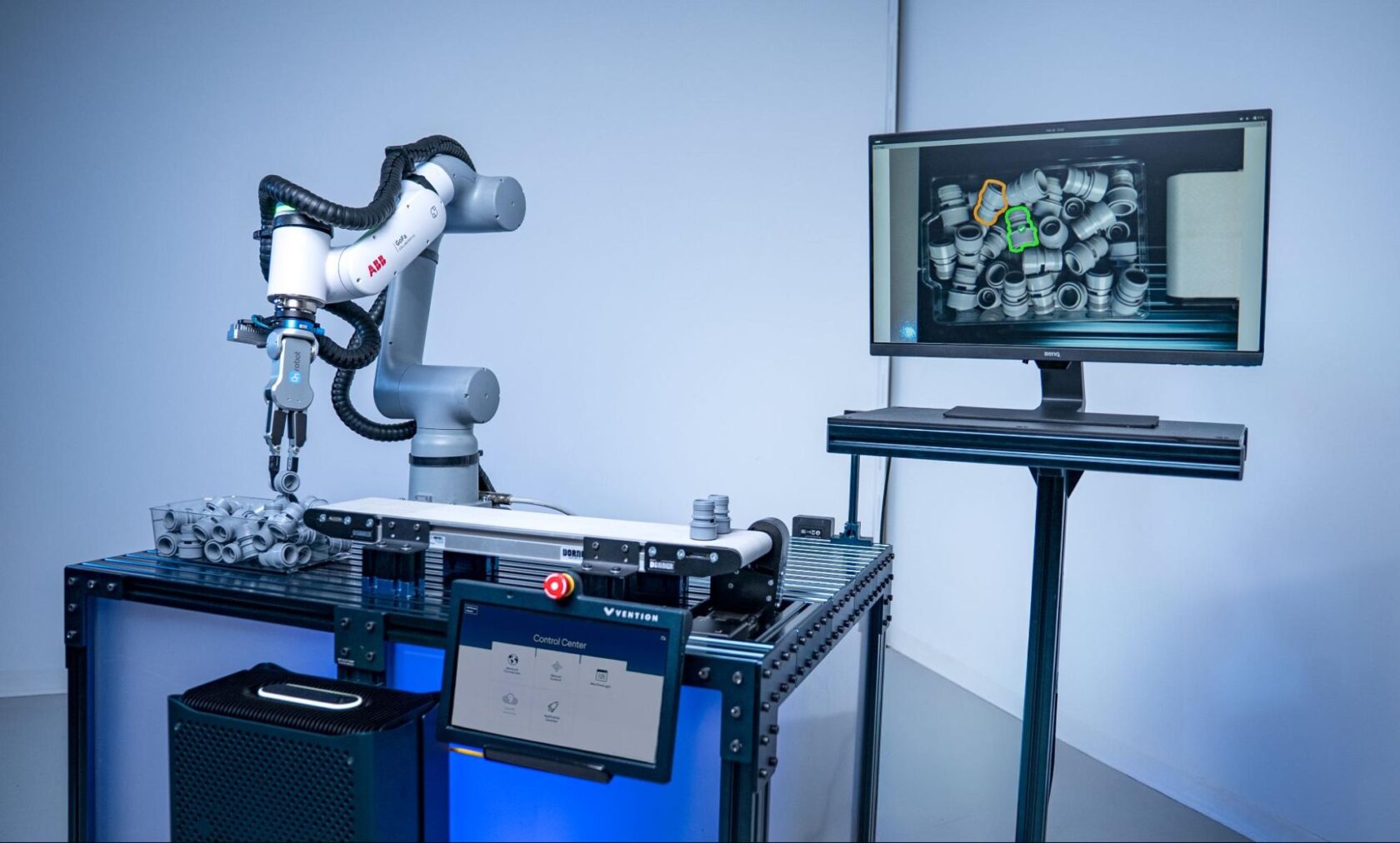

Learn more about the latest robotics advancements by joining NVIDIA at Automatica, running through Friday, June 27.










 NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)
NVIDIA GeForce NOW (@NVIDIAGFN)