NVIDIA Grows Quantum Computing Ecosystem With Taiwan Manufacturers and Supercomputing
Quantum computing promises to shorten the path to solving some of the world’s biggest computational challenges, from scaling in-silico drug design to optimizing otherwise impossibly complex, large-scale logistics problems.
Integrating quantum hardware into state-of-the-art AI supercomputers — forming accelerated quantum supercomputers — helps speed the scaling of today’s quantum processors into helpful devices for solving these complex challenges.
At the COMPUTEX trade show, NVIDIA underscored how its work with partners across the Taiwan supercomputing ecosystem is advancing quantum computing toward accelerated quantum supercomputers.
Leading hardware developers are working with NVIDIA to equip quantum researchers with tools to make significant contributions in the field.
Atlantic Quantum, the University of Edinburgh,, the University of Oxford, Quantum Circuits Inc., QuEra Computing and Yale University anticipate receiving NVIDIA Grace Hopper Superchips from Supermicro to explore and refine the intersections between AI supercomputing and quantum computing.
Compal announced its CGA-QX platform, built using the NVIDIA CUDA-Q platform, to accelerate the simulation of quantum optimization problems. The platform has been adopted by the Taiwanese National Science and Technology Council and made available to researchers from universities across Taiwan.
Quanta has employed NVIDIA CUDA-Q to experiment with physical quantum hardware, using the platform’s state vector simulations to verify and validate existing quantum processors. This allows Quanta to understand the details of noise in its systems and assess how well they work for use cases of interest.
NVIDIA is also working with supercomputing centers to advance accelerated quantum supercomputing.
Taiwan’s National Center for High-Performance Computing (NCHC) announced a new supercomputer for quantum research. Built by ASUS, the AI supercomputer at NCHC will feature NVIDIA HGX H200 systems with over 1,700 GPUs, two NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 rack-scale systems and an NVIDIA HGX B300 system built on the next-generation NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra platform — interconnected by NVIDIA Quantum InfiniBand networking. Announced today at COMPUTEX, it’s expected to go live later this year.
NCHC is enabling over 20 companies working in quantum computing — collaborating under what’s known as the National Quantum Team. NVIDIA CUDA-Q is being used at the center to explore quantum solutions for applications ranging from machine learning to chemistry.
In Japan, AIST’s ABCI-Q — the world’s most powerful supercomputer dedicated to quantum workloads — integrates an NVIDIA supercomputer with more than 2,000 NVIDIA H100 GPUs with quantum processors from Fujitsu, QuEra Computing and OptQC.
Increased availability of these quantum-AI platforms is poised to accelerate the breakthroughs researchers can make in quantum computing — including developing new error correcting codes, integrating quantum processors within AI supercomputing and simulating low noise designs of quantum hardware.
Learn more about NVIDIA’s work advancing accelerated quantum supercomputing at NVIDIA GTC Taipei, running May 21-22.
That’s One Smart Hospital! Taiwan Medical Centers Deploy Life-Saving Innovations With NVIDIA System-Builder Partners
Leading healthcare organizations across the globe are using agentic AI, robotics and digital twins of medical environments to enhance surgical precision, boost workflow efficiency, improve medical diagnoses and more.
Physical AI and humanoid robots in hospitals have the potential to automate routine tasks, assist with patient care and address workforce shortages.
This is especially crucial in places where challenges to optimal healthcare services are paramount. Such challenges include hospital overcrowding, an aging population, rising healthcare costs and a shortage of medical professionals, all of which are affecting Taiwan, as well as many other regions and countries.
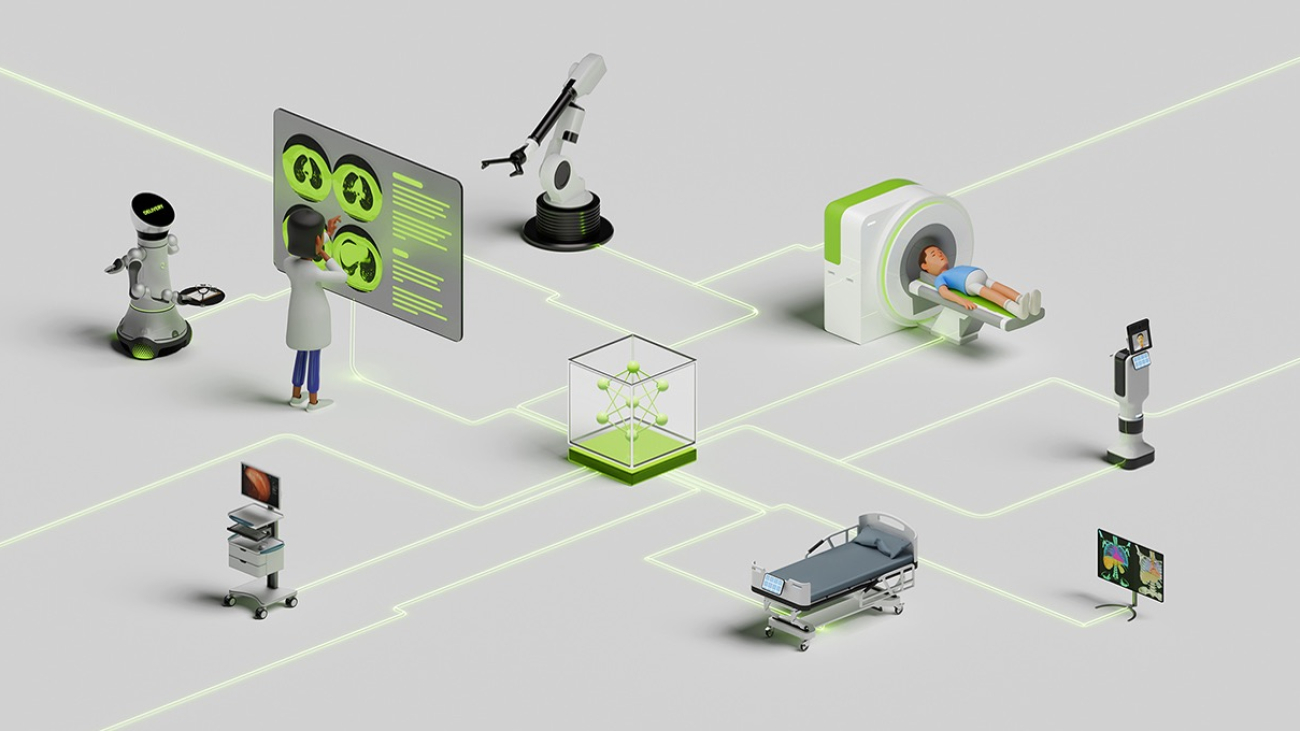
At the COMPUTEX trade show in Taipei, NVIDIA today showcased how leading Taiwan medical centers are collaborating with top system builders to integrate smart hospital technologies and other AI-powered healthcare solutions that can help reduce these issues and save millions of lives.
Cathay General Hospital, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (CGMH), National Taiwan University Hospital (NTUH) and Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH) are among the top centers in the region pioneering healthcare AI innovation.
Deployed in collaboration with leading system builders such as Advantech, Onyx, Foxconn and YUAN, these solutions tap into NVIDIA’s agentic AI and robotics technologies, including the NVIDIA Holoscan and IGX platforms, NVIDIA Jetson for embedded computing and NVIDIA Omniverse for simulating virtual worlds with OpenUSD.
CGMH Boosts AI-Powered Medical Imaging
With an average of 8.2 million outpatient visits and 2.4 million hospitalizations a year, CGMH estimates that a third of the Taiwanese population has sought treatment at its vast network of hospitals in Taipei and seven other cities.
The organization is pioneering smart hospital innovation by enhancing surgical precision and workflow efficiency through advanced, AI-powered colonoscopy workflow solutions, developed in collaboration with Advantech and based on the NVIDIA Holoscan platform, which includes the Holoscan SDK and the Holoscan Sensor Bridge running on NVIDIA IGX.
NVIDIA Holoscan is a real-time sensor processing platform for edge AI compute, while NVIDIA IGX offers enterprise-ready, industrial edge AI purpose-built for medical environments.
Using these platforms, CGMH is accelerating AI integration in its colonoscopy diagnostics procedures. Deployed in gastrointestinal consultation rooms, the AI-powered tool collects colonoscopy streams to train a customized model built on Holoscan and provides real-time colonic polyps identification and classification.
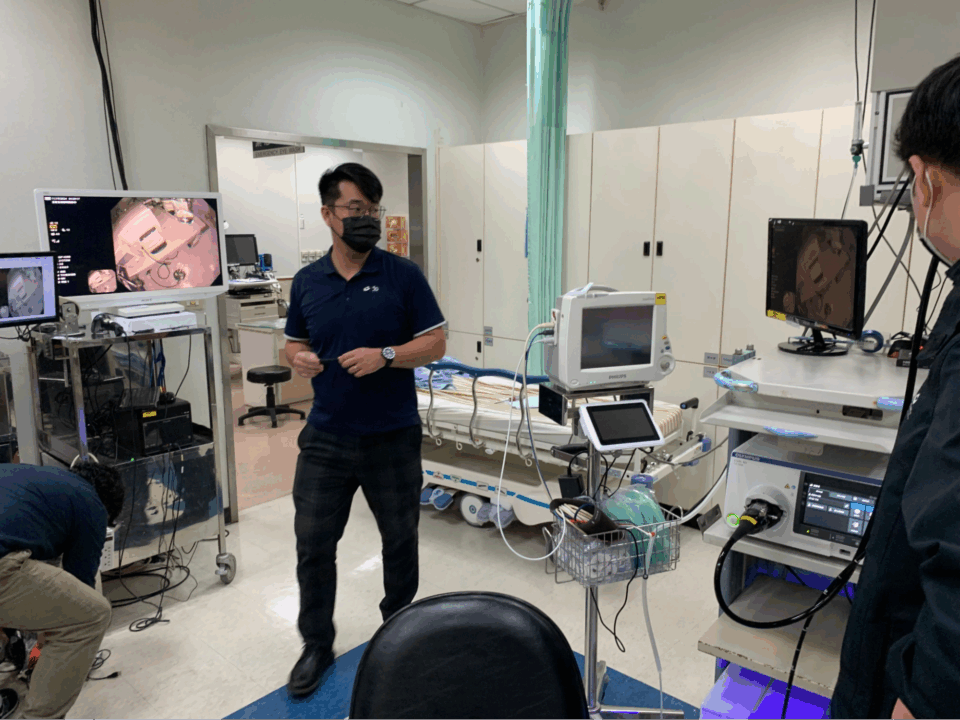
CGMH’s AI infrastructure — comprising NVIDIA accelerated computing, NVIDIA DGX systems, the MONAI framework, NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM open-source library, NVIDIA Dynamo inference framework, and the NVIDIA NeMo and Clara platforms — enables accelerated research and development across the organization.
CGMH serves nearly 50 AI agent models that daily help the hospital analyze medical imaging, improving diagnostic accuracy, throughput and real-time inference at scale. For example, NVIDIA Triton-powered AI sped newborn examination record processing by 10x.
Cathay General Hospital Improves Diagnostics With AI
Cathay General Hospital, a Taipei-based healthcare center that provides hospital management and medical services, has worked with Onyx and software provider aetherAI to develop an AI-assisted colonoscopy system that highlights lesions, detects hard-to-spot polyps and issues alerts to help physicians with diagnoses.
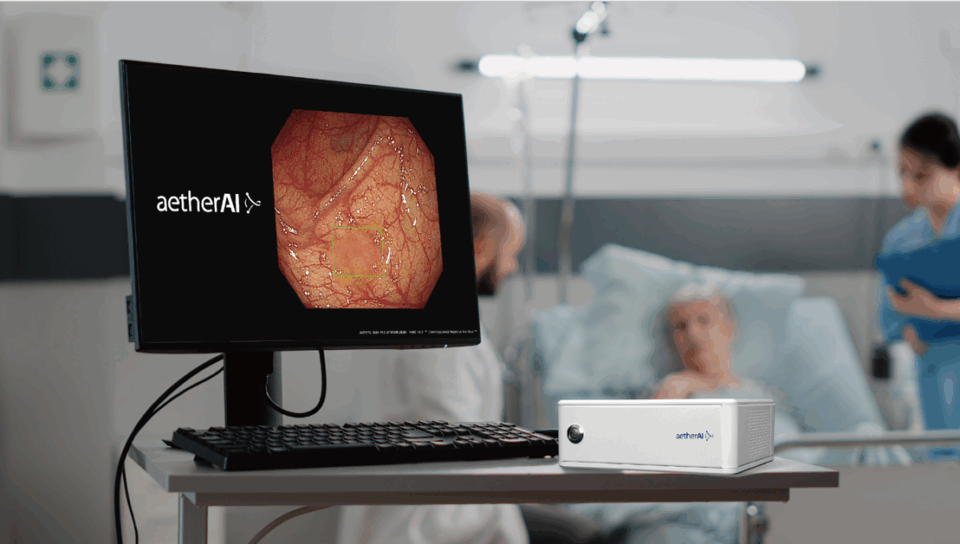
Powered by a compact, plug-and-play AI BOX device — built with the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Xavier module — the AI system is trained on over 400,000 high-quality, physician-annotated images collected from patients with diverse and severe lesions over four years.
Studies have shown the system can achieve up to 95.8% accuracy and sensitivity while improving adenoma detection rates by as much as 30%. These enhancements assist physicians in reducing diagnostic errors and making more informed treatment decisions, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes.
NTUH Detects Liver Tumors, Cardiovascular Risks With AI
In the 100+ years since its founding, NTUH has nurtured countless professionals in medicine and is renowned for its trusted clinical care. The national teaching hospital is now adopting AI imaging to more quickly, accurately diagnose patients.
NTUH’s HeaortaNet model, trained on more than 70,000 axial images from 200 patients, automates CT scan segmentation of the heart, including the aorta and other arteries, in 3D, enabling rapid analysis of risks for cardiovascular disease. The model, which achieves high segmentation accuracy for the pericardium and aorta, significantly reduced data processing time per case from an hour to about 0.4 seconds.
In addition, NTUH collaborated with the Good Liver Foundation and system builder YUAN to develop a diagnostic-assistance system for liver cancer detection during ultrasounds. It taps into an NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX module and a deep learning model trained on more than 5,000 annotated ultrasound images to identify malignant and benign liver tumors in real time.

NVIDIA DeepStream and TensorRT SDKs accelerate the system’s deep learning model, ultimately helping clinicians detect tumors earlier and more reliably. In addition, NTUH is using NVIDIA DGX to train AI models for its system that detects pancreatic cancer from CT scans.
TCVGH Streamlines Multimodal Imaging and Clinical Documentation Workflows With AI
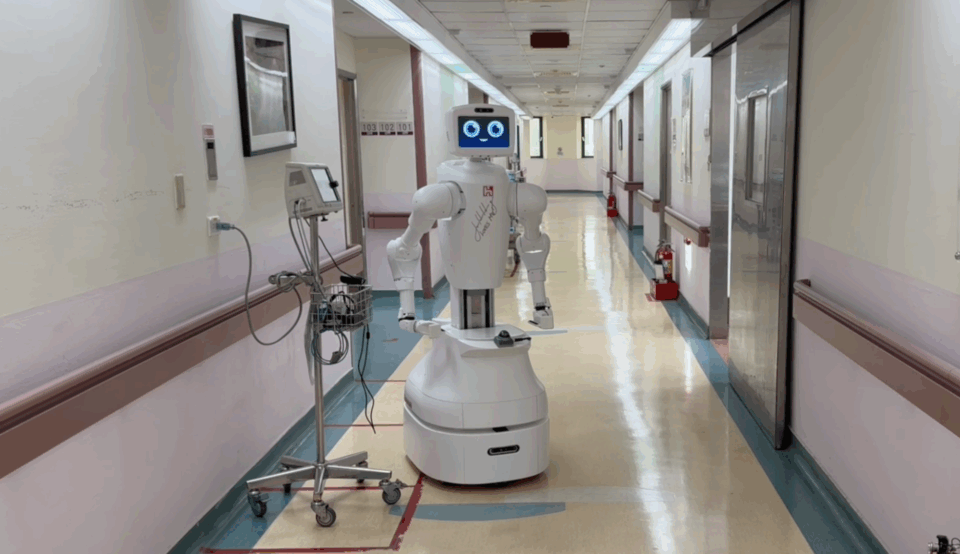
Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH), a medical center and a teaching hospital administered by the Veterans Affairs Council in Taipei, has partnered with Foxconn to build physical and digital robots to augment staffing, improving clinician productivity and patient experiences.
Foxconn developed an AI system that can analyze medical images and spot signs of breast cancer earlier than traditional methods, using NVIDIA Hopper GPUs, NVIDIA DGX systems and the MONAI framework. By tapping into clinical data and multimodal AI imaging, the system creates 3D virtual breast models, quickly highlighting areas of concern in scans to help radiologists make faster, more confident decisions.
Foxconn is also working with TCVGH to build smart hospital solutions like the AI nursing collaborative robot Nurabot and tapping into NVIDIA Omniverse to create real-time digital twins of hospital environments, including nursing stations, patient wards and corridors. These digital replicas serve as high-fidelity simulations where Jetson-powered service robots can be trained to autonomously deliver medical supplies throughout the hospital, ultimately improving care efficiency.

In addition, TCVGH has developed and deployed its Co-Healer system, which integrates the Taiwanese native large language model TAIDE-LX-7B to streamline clinical documentation processes with agentic AI.
Co-Healer, built on the NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX module, processes and helps summarize medical documents — such as nursing progress notes and health education materials — and supports medical exam preparation by providing students with instant access to nursing guidelines and patient-specific protocols for clinical procedures and diagnostic tests. This helps healthcare workers alleviate burnout while giving patients a clearer understanding of their diagnoses.
Learn more about the latest AI advancements in healthcare at NVIDIA GTC Taipei, running May 21-22 at COMPUTEX.
NVIDIA-Powered Supercomputer to Enable Quantum Leap for Taiwan Research
Researchers across Taiwan are tackling complex challenges in AI development, climate science and quantum computing. Their work will soon be boosted by a new supercomputer at Taiwan’s National Center for High-Performance Computing that’s set to deliver over 8x more AI performance than the center’s earlier Taiwania 2 system.
The AI supercomputer at NCHC is slated to feature NVIDIA HGX H200 systems with over 1,700 GPUs, two NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 rack-scale systems and an NVIDIA HGX B300 system built on the NVIDIA Blackwell Ultra platform — interconnected by NVIDIA Quantum InfiniBand networking. Announced today at COMPUTEX, it’s expected to go live later this year.
NCHC also plans to deploy a set of NVIDIA DGX Spark personal AI supercomputers and a cluster of NVIDIA HGX systems in the cloud.
Researchers from academic institutions, government agencies and small businesses in Taiwan will be able to apply for access to the new system to accelerate innovative projects.
“The new NCHC supercomputer will drive breakthroughs in sovereign AI, quantum computing and advanced scientific computation,” said Chau-Lyan Chang, director general of NCHC. “It’s designed to empower Taiwan’s technological autonomy, fostering cross-domain collaboration and global AI leadership.”
Developing Local Language Models for Sovereign AI
The new supercomputer will support projects like Taiwan AI RAP, a generative AI application development platform. Taiwan AI RAP aims to support the rapid development of AI products by offering startups, researchers and enterprises access to customized models that reflect local cultural and linguistic nuances.
Among the platform’s offerings are models created by Taiwan’s Trustworthy AI Dialogue Engine, or TAIDE — a public sector initiative to build Taiwanese large language models (LLMs) for tasks including natural language processing, intelligent customer service and translation.
Collaborators providing text, images, audio and video data for the initiative include local governments, news organizations and public departments such as the Ministry of Education and Ministry of Culture.
To support the creation of sovereign AI applications, TAIDE currently offers developers access to a collection of Llama3.1-TAIDE foundation models. The team is building additional sovereign AI LLM services using NVIDIA Nemotron models.
A professor at National Tainan University is using the TAIDE model to power a conversational AI robot that speaks Taiwanese and English with elementary and middle school students. It’s been used by over 2,000 students, teachers and parents to date. Another professor tapped the model to generate high-quality educational materials, shortening lesson preparation time for teachers.
In healthcare, research teams in Taiwan used the TAIDE model to develop an AI chatbot with retrieval-augmented generation that helps case managers deliver timely, accurate medical information to patients with major injuries and illnesses. And the Epidemic Prevention Center at Taiwan’s Centers for Disease Control is training the model to generate news summaries to support the tracking and prevention of how diseases spread.
Speeding Scientific Research in Climate and Beyond
In climate research, NCHC supports researchers using the NVIDIA Earth-2 platform to advance atmospheric science. These researchers are tapping Earth-2’s CorrDiff AI model to sharpen the precision of coarse-resolution weather models, and DeepMind’s GraphCast model in NVIDIA PhysicsNeMo for global weather forecasting.
They’re also adopting the NVIDIA NIM microservice for FourCastNet, an NVIDIA model that predicts global atmospheric dynamics of weather and climate variables, and using NVIDIA GPUs to accelerate the simulation of numerical weather prediction models.
With the new supercomputer, the researchers will be able to run more complex simulations and accelerate the pace of AI training and inference.
Advancing Quantum Innovation
NCHC researchers are also advancing quantum research using the NVIDIA CUDA-Q platform and NVIDIA cuQuantum library targeting applications in quantum machine learning, chemistry, finance, cryptography and more.
The research institute has developed Quantum Molecular Generator, a tool that generates valid chemical molecules, using quantum circuits and the CUDA-Q platform. It’s also created cuTN-QSVM, an open-source tool built on the cuQuantum library that accelerates large-scale quantum circuit simulations.
The tool enables researchers to tackle more complex problems, offering linear scalability and supporting hybrid quantum computing systems to help accelerate the development of large-scale quantum algorithms.
NCHC researchers recently used cuTN-QSVM to perform a record-breaking 784-qubit simulation for a quantum machine learning algorithm. The institute also plans to build a hybrid quantum-accelerated computing system by integrating NVIDIA DGX Quantum systems.
Learn more about Taiwan’s National Center for High-Performance Computing at NVIDIA GTC Taipei, taking place May 21-22.
Watch the COMPUTEX keynote by NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang.
NVIDIA Grace CPU C1 Gains Broad Support in Edge, Telco and Storage
NVIDIA is highlighting significant momentum for its new Grace CPU C1 this week at the COMPUTEX trade show in Taipei, with a strong showing of support from key original design manufacturer partners.
The expanding NVIDIA Grace CPU lineup, including the powerful NVIDIA Grace Hopper Superchip and the flagship Grace Blackwell platform, is delivering significant efficiency and performance gains for major enterprises tackling demanding AI workloads.
As AI continues its rapid advancement, power efficiency has become a critical factor in data center design for applications ranging from large language models to complex simulations.
The NVIDIA Grace architecture is directly addressing this challenge.
NVIDIA Grace Blackwell NVL72, a rack-scale system integrating 36 NVIDIA Grace CPUs and 72 NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, is being adopted by major cloud providers to accelerate AI training and inference, including complex reasoning and physical AI tasks.
The NVIDIA Grace architecture now comes in two key configurations: the dual-CPU Grace Superchip and the new single-CPU Grace CPU C1.
The C1 variant is gaining significant traction in edge, telco, storage and cloud deployments where maximizing performance per watt is paramount.
The Grace CPU C1 boasts a claimed 2x improvement in energy efficiency compared with traditional CPUs, a vital advantage in distributed and power-constrained environments.
Leading manufacturers like Foxconn, Jabil, Lanner, MiTAC Computing, Supermicro and Quanta Cloud Technology support this momentum, developing systems using the Grace CPU C1’s capabilities.
In the telco space, the NVIDIA Compact Aerial RAN Computer, which combines the Grace CPU C1 with an NVIDIA L4 GPU and NVIDIA ConnectX-7 SmartNIC, is gaining traction as a platform for distributed AI-RAN, meeting the power, performance and size requirements for deployment at cell sites.
NVIDIA Grace is also finding a home in storage solutions, with WEKA and Supermicro deploying it for its high performance and memory bandwidth.
Real-World Impact
NVIDIA Grace’s benefits aren’t theoretical — they’re tangible in real-world deployments:
- ExxonMobil is using Grace Hopper for seismic imaging, crunching massive datasets to gain insights on subsurface features and geological formations.
- Meta is deploying Grace Hopper for ad serving and filtering, using the high-bandwidth NVIDIA NVLink-C2C interconnect between the CPU and GPU to manage enormous recommendation tables.
- High-performance computing centers such as the Texas Advanced Computing Center and Taiwan’s National Center for High-Performance Computing are using the Grace CPU in their systems for AI and simulation to advance research.
Learn more about the latest AI advancements at NVIDIA GTC Taipei, running May 21-22 at COMPUTEX.
Semiconductor Industry Accelerates Design Manufacturing With NVIDIA Blackwell and CUDA-X
TSMC, Cadence, KLA, Siemens and Synopsys are advancing semiconductor manufacturing by adopting the NVIDIA CUDA-X and NVIDIA Blackwell platforms.
NVIDIA Blackwell GPUs, NVIDIA Grace CPUs, high-speed NVIDIA NVLink fabrics and switches, and domain-specific NVIDIA CUDA-X libraries like NVIDIA cuDSS and NVIDIA cuLitho are improving computational lithography and device simulation for advanced chip manufacturing.
“Our collaboration with NVIDIA represents a significant advancement in semiconductor process simulation,” said Jeff Wu, fellow and director for the technology computer-aided design division at TSMC. “The computational acceleration from CUDA-X libraries and NVIDIA Grace Blackwell will expedite process development by simulating complex manufacturing processes and device behaviors at lower cost.”
NVIDIA cuLitho and Blackwell speed up lithography by up to 25x. GPU acceleration enables leading lithography providers and semiconductor manufacturers such as TSMC to predict and correct lithography issues before production at an unprecedented speed.
Earlier this month, electronic design automation (EDA) software and services provider Cadence announced its Millennium M2000 platform, built exclusively on NVIDIA Blackwell for the EDA market. The M2000 is a scalable turnkey solution for deploying NVIDIA Grace Blackwell and CUDA-X libraries with a fully accelerated portfolio of Cadence design tools.
Cadence is also one of the first to adopt NVIDIA NVLink Fusion, enabling custom silicon scale-up to meet the requirements of demanding workloads for model training and agentic AI inference. By adopting NVLink Fusion, Cadence allows hyperscalers to optimize and validate across the entire design spectrum.
This month, Cadence announced the Millennium M2000 AI Supercomputer to transform silicon, system and drug design. Based on the NVIDIA Blackwell platform, options include the NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 system for tackling massive system-on-a-chip, 3D-IC, and subsystem implementation and signoff using Cadence Cerebrus AI Studio and Cadence multiphysics system analysis tools, as well as the new NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell Server Edition GPU for smaller chip designs and simulations.
“Our collaboration with NVIDIA has always been about pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in both electronic design automation and system design and analysis,” said Michael Jackson, corporate vice president and general manager of the system design and analysis group at Cadence. “The Millennium M2000 platform, built exclusively on NVIDIA Blackwell, isn’t just about faster simulation — it’s about redefining the infrastructure for AI-driven innovation, enabling what was previously impossible.”
Siemens is harnessing the parallel processing power of the NVIDIA CUDA-X libraries and the groundbreaking performance of the Grace Blackwell platform to significantly accelerate its Calibre platform.
This integration enables unprecedented speed and accuracy in critical semiconductor manufacturing steps, including optical proximity correction with nanometer precision, comprehensive physical verification, robust design for manufacturability analysis, thorough reliability verification and seamless integration and automation across the design-to-manufacturing flow.
“Leveraging NVIDIA CUDA-X and Grace Blackwell in our Calibre platform enables faster, more efficient optical proximity correction without sacrificing accuracy for advanced semiconductor nodes,” said Mike Ellow, CEO of Siemens EDA. “This is especially important as chip complexity continues to grow.”
Additionally, Synopsys, a leading EDA software and services provider, is using NVIDIA CUDA-X libraries and Blackwell for its EDA tools, including Synopsys PrimeSim, Proteus, S-Litho, Sentaurus Device and QuantumATK. By integrating with CUDA-X libraries, Synopsys achieved new benchmark results for Sentaurus Device, QuantumATK, and S-Litho on the NVIDIA B200, demonstrating a 12x, 15x and 20x scale-up, respectively, versus comparable CPU infrastructure.
In addition, Synopsys recently announced at NVIDIA GTC that they project Synopsys PrimeSim to run 30x faster and Synopsys Proteus to run 20x faster on NVIDIA Blackwell platforms.
“Synopsys has a long history of collaborating with NVIDIA on accelerating our EDA solutions to maximize the capabilities of engineering teams. Building on our industry-first approach, Synopsys is leveraging NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture across our TCAD, computational lithography and atomistic simulation products to unlock unprecedented performance gains,” said Sanjay Bali, senior vice president of strategy and product management at Synopsys. “By integrating NVIDIA’s CUDA-X libraries and Blackwell architecture into our industry-leading simulation solvers, we’ve achieved transformative speedups and redefined how EDA is enabling semiconductor manufacturing innovation.”
Semiconductor process control equipment manufacturer KLA and NVIDIA have worked together for over a decade to advance KLA’s physics-based AI with optimized high-performance computing solutions that tap into GPUs and the CUDA ecosystem.
The value of process control in semiconductor manufacturing is increasing due to AI-driven trends, such as more complex designs, accelerated product cycles, higher value wafer volumes and growing advanced packaging demand. KLA’s industry-leading inspection and metrology systems capture and process images by running complex AI algorithms to find the most critical semiconductor defects at lightning-fast speeds.
KLA is looking forward to evaluating the NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000 Blackwell Server Edition with CUDA-X libraries for certain markets to further accelerate inference workloads powering the semiconductor chip manufacturing process.
By embedding NVIDIA Blackwell into EDA, manufacturing and process control, NVIDIA is helping the semiconductor industry deliver the next generation of high-performance chips faster.
Learn more about the latest AI advancements at NVIDIA GTC Taipei, running May 21-22 at COMPUTEX.
AI Blueprint for Video Search and Summarization Now Available to Deploy Video Analytics AI Agents Across Industries
The age of video analytics AI agents is here.
Video is one of the defining features of the modern digital landscape, accounting for over 50% of all global data traffic. Dominant in media and increasingly important for enterprises across industries, it is one of the largest and most ubiquitous data sources in the world. Yet less than 1% of it is analyzed for insights.
Nearly half of global GDP comes from physical industries — spanning energy to automotive and electronics. With labor shortage concerns, manufacturing onshoring efforts and rising demand for automation, video analytics AI agents will play a more critical role than ever, helping bridge the physical and digital worlds.
To accelerate the development of these agents, NVIDIA today is making the AI Blueprint for video search and summarization (VSS), powered by the NVIDIA Metropolis platform, generally available — giving developers the tools to create and deploy highly capable AI agents for analyzing vast sums of real-time and archived videos.
A wave of vision AI agents and productivity assistants powered by vision language models (VLMs) are coming online. Combining powerful computer vision models with the skills of super intelligent large language models (LLMs), these video analytics AI agents allow enterprises to easily see, search and summarize huge volumes of video. By analyzing videos in real time or reviewing terabytes of recorded video, video analytics AI agents are unlocking unprecedented value and opportunities across a range of important industries.
Manufacturers and warehouses are using AI agents to help increase worker safety and productivity. For example, agents can help distribute forklifts and position workers for optimal efficiency. Smart cities are deploying video analytics AI agents to reduce traffic congestion and increase safety, and the uses go on and on.
A Blueprint to Create Diverse Fleets of Video Analytics AI Agents
The VSS blueprint is built on top of the NVIDIA Metropolis platform and boosted by VLMs and LLMs such as NVIDIA VILA and NVIDIA Llama Nemotron, NVIDIA NeMo Retriever microservices, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) — a technique that connects LLMs to a company’s enterprise data.
The VSS blueprint incorporates the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform, including NVIDIA NIM microservices for VLMs, LLMs and advanced AI frameworks for RAG. With the VSS blueprint, users can summarize a video 100x faster than watching in real time. For example, an hourlong video can be summarized in text in less than one minute.
The VSS blueprint offers a host of powerful features designed to provide robust video understanding, performance and scalability.
This release introduces expanded hardware support, including the ability to deploy on a single NVIDIA A100 or H100 GPU for smaller workloads, offering greater flexibility in resource allocation. The blueprint can also be deployed at the edge on the NVIDIA RTX 6000 PRO and NVIDIA DGX Spark computing platforms.
The VSS blueprint can process hundreds of live video streams or burst clips simultaneously. In addition to visual understanding, it offers audio transcription. Converting speech to text adds contextual depth in scenarios where audio is critical — such as training videos, keynotes or team meetings.
Industry Leaders Deploy Video Analytics AI Agents to Drive Business Value
Everyone from the world’s leading manufacturers to smart cities and sports leagues are using the VSS blueprint to develop AI agents for optimizing operations.
Pegatron, a leading electronics manufacturing company, uses the VSS blueprint to study operating procedures and train employees on best practices. The company is also integrating the blueprint into its PEGAAi platform so organizations can build AI agents to transform manufacturing processes.
These agents can ingest and analyze massive volumes of video, enabling advanced capabilities like automated monitoring, anomaly detection, video search and incident reporting. Pegatron’s Visual Analytics Agent can be used to understand operating procedures for printed circuit board assembly and identify when actions are correct or incorrect. To date, the agents have reduced Pegatron’s labor costs by 7% and defect rates by 67%.
Additional leading Taiwanese semiconductor and electronics manufacturers are building AI agents and digital twins to optimize their planning and operational applications.
Kaohsiung City, Taiwan, is using a unified smart city vision AI application developed by its partner, Linker Vision, to improve incident response times. Previously, city departments such as waste management, transportation and emergency response were isolated by siloed infrastructure — leading to slow response times due to lack of access to critical information.
Powered by the VSS blueprint, Linker Vision’s AI-powered application has agents that combine real-time video analytics with generative AI to not just detect visual elements but also understand and narrate complex urban events like floods or traffic accidents.
Linker Vision currently delivers timely insights to 12 city departments and is on track to scale from 30,000 city cameras to over 50,000 by 2026. These insights are providing improved situational awareness and data-driven decision-making across city services, and reducing incident response times by up to 80%.
The National Hockey League used the VAST InsightEngine with the VSS blueprint to streamline and accelerate vision AI workflows. It manages massive volumes of game footage.
With the VAST InsightEngine, the NHL is positioned to search through petabytes of video in sub-seconds, enabling near-instant retrieval of highlights and in-game moments. AI-driven agentic workflows further enhance content creation by automatically clipping, tagging and assembling video content for ease of access and use.
In the future, the League could potentially use real-time AI reasoning to enable tailored insights — such as player stats, strategy analyses or fantasy recommendations — generated dynamically during live games. This end-to-end automation could transform how media is created, curated and delivered, setting a new standard for AI-driven sports content production.
Siemens is using its Industrial Copilot for Operations to assist factory floor workers with equipment maintenance tasks, error handling and performance optimization. This generative AI-powered assistant offers real-time answers to equipment errors using information about operational and document data.
The copilot was built with a fusion of VSS components like VLMs, LLMs and NVIDIA NeMo microservices. The Industrial Copilot has resulted in rapid decision-making and reduced machine downtime. Siemens has reported a 30% increase in productivity, with the potential to reach 50%.
Supported by an Expanding Partner Ecosystem Creating Sophisticated AI Agents
NVIDIA partners are using the VSS blueprint to expedite the creation of agentic AI video analytics capabilities for their workflows, reducing development time from months to weeks.
Superb AI, a leader in intelligent video analytics, set up a sophisticated airport operations project at Incheon Airport to reduce passenger wait times in a matter of weeks. In Malaysia, solution provider ITMAX is building advanced visual AI agents with the VSS blueprint for the City of Kuala Lumpur to improve overall city management and reduce incident response times.
In the advertising sector, PYLER integrated the VSS blueprint into its brand safety (AiD) and ad targeting (AiM) solutions in just a few weeks. Using AiD and AiM, Samsung Electronics increased advertising effectiveness with brand- and product-aligned, high-value ad placements. BYD saw its ad-click through rates increase 4x by targeting contextually relevant and positive content, while Hana Financial Group surpassed multiple brand campaign goals.
Fingermark is the application provider of Eyecue, a real-time computer vision platform used by quick service restaurants. Fingermark is adding the VSS blueprint into Eyecue to turn video footage into clear, actionable insights regarding drive-thru wait times, service bottlenecks and staff-related incidents at scale.
Try the VSS blueprint on build.nvidia.com and read this technical blog for more details.
NVIDIA Expands Omniverse Blueprint for AI Factory Digital Twins With New Ecosystem Integrations, Development Tools
Empowering engineering teams with more tools for building AI factories, NVIDIA today announced a significant expansion of the NVIDIA Omniverse Blueprint for AI factory digital twins, now available as a preview.
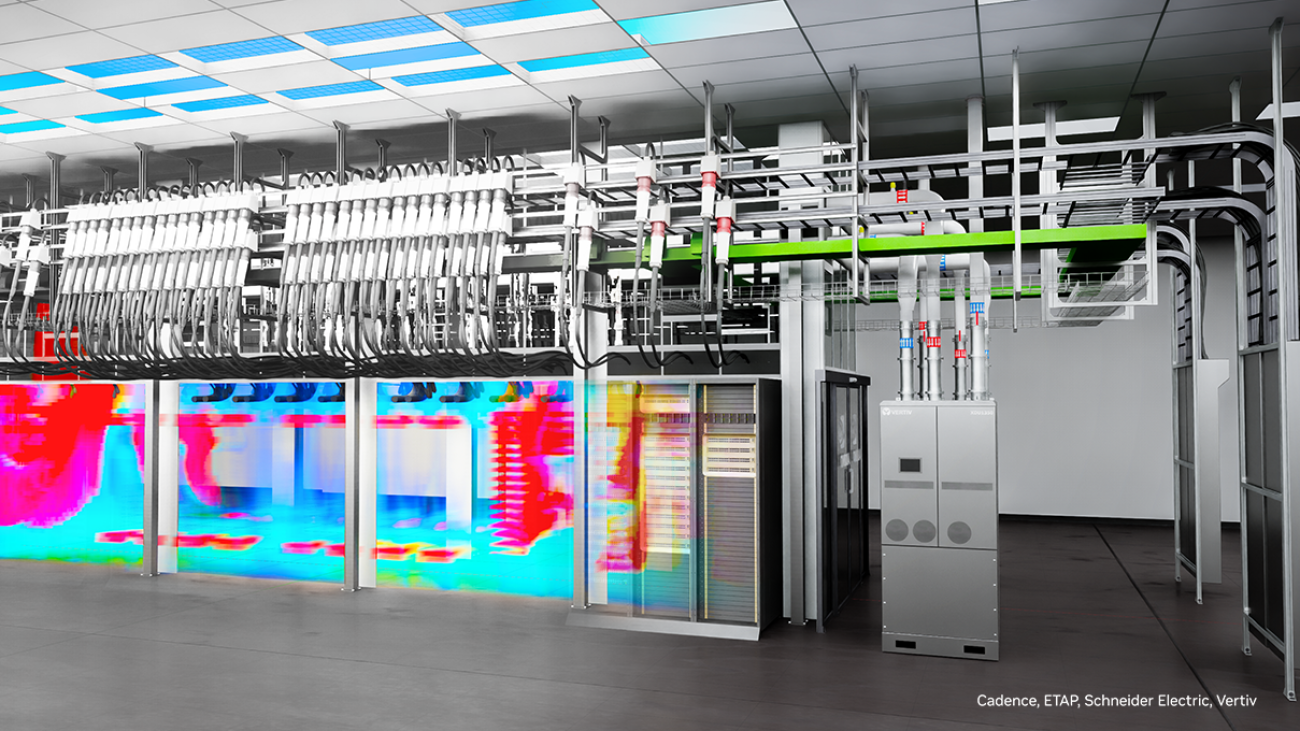
The blueprint features new integrations across the AI factory power, cooling and networking ecosystems with industry leaders Delta Electronics, Jacobs and Siemens, joining existing partners Cadence, Schneider Electric with ETAP and Vertiv.
This growing ecosystem unifies the design and simulation of billions of components required to build digital twins of AI factories. The expanded blueprint will equip engineering teams to design, simulate and optimize entire AI factories in physically accurate virtual environments, enabling early issue detection and the development of smarter, more reliable facilities.
Built on reference architectures for NVIDIA GB200 NVL72-powered AI factories, the blueprint taps into Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD) asset libraries. This allows developers to aggregate detailed 3D and simulation data representing all aspects of the data center into a single, unified model, enabling them to design and simulate advanced AI infrastructure optimized for efficiency, throughput and resiliency.
AI Factory Ecosystem Teams With NVIDIA
The Omniverse Blueprint for AI factory digital twins brings together diverse partners and tools to optimize the design, simulation, deployment and operations of AI factories. Today, NVIDIA announced that new partners are contributing to the framework.
Siemens is building 3D models according to the blueprint and engaging with the simulation-ready, or SimReady, standardization effort, while Delta Electronics is adding models of its equipment. Because these are built with OpenUSD, users get accurate simulations of their facility equipment. Jacobs is helping test and optimize the end-to-end blueprint workflow.
They join leaders in data center power and cooling solutions like Schneider Electric with ETAP and Vertiv, which contribute SimReady assets to populate the digital twin of the AI factory with 3D models of power, cooling and mechanical systems.
“As AI factories continue to scale at an unprecedented pace, the energy demands they generate are reshaping the entire digital infrastructure landscape,” says Tanuj Khandelwal, CEO of ETAP. “Using the Omniverse Blueprint and SimReady assets, customers can test and optimize energy efficiency for the complexity and intensity of their AI workloads before even breaking ground.”
Connections to the Cadence Reality Digital Twin Platform and ETAP provide thermal and power simulation, enabling engineering teams to test and optimize power, cooling and networking long before construction begins. These contributions help NVIDIA and its partners reshape how AI infrastructure is built to achieve smarter designs, avoid downtime and get the most out of AI factories.
“Digital twins are fundamental to meet the escalating global demand for AI factories,” said Ben Gu, corporate vice president of R&D for multiphysics system analysis at Cadence. “The integration of the Cadence Reality Digital Twin Platform with the NVIDIA Omniverse Blueprint transforms the entire engineering process to design AI factories more efficiently and operate them more effectively than ever before. We are excited to continue our full-stack collaboration with NVIDIA.”
Building SimReady Assets for AI Factories
The OpenUSD-based models within the blueprint are inherently SimReady, designed from the ground up to be physics-based. This is especially valuable for developing and testing physical AI and agentic AI within these AI factories, enabling rapid and large-scale industrial AI simulations of power and cooling systems, building automation and overall IT operations.
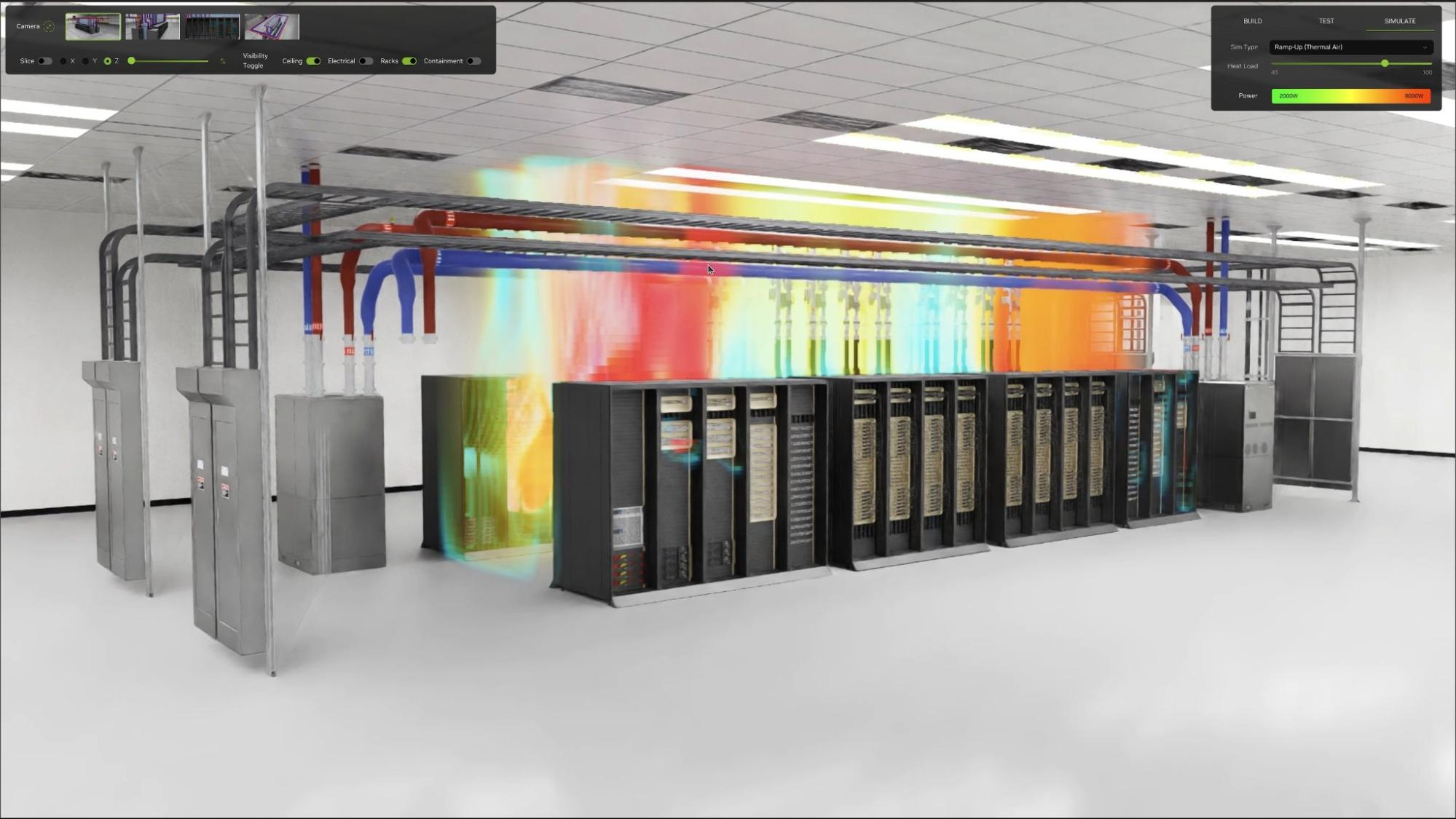

A key enhancement to this blueprint is the SimReady standardization workflow. Originally developed as a SimReady standardization proposal to streamline NVIDIA’s internal creation of OpenUSD assets, this now publicly available, industry-agnostic resource offers standardized requirements and processes for developing SimReady capabilities. It empowers data center developers and owners to efficiently establish, optimize and rigorously test their own digital twins of critical infrastructure, particularly for electrical and thermal management within AI factories.
A Smarter Road to AI Infrastructure
The expansion of the NVIDIA Omniverse Blueprint for AI factory digital twins marks a significant leap forward in how engineers design, simulate and build the sophisticated infrastructure required for industrial AI.
By providing a unified and physically accurate digital twin, built on the robust foundation of OpenUSD and guided by SimReady standardization, this blueprint enables the industry to de-risk development, optimize performance and accelerate the deployment of next-generation AI factories.
Learn more about NVIDIA Omniverse and preview the Omniverse Blueprint for AI factory digital twins. Watch the COMPUTEX keynote from NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang and learn more at NVIDIA GTC Taipei.
See notice regarding software product information.
NVIDIA Omniverse Digital Twins Help Taiwan Manufacturers Drive Golden Age of Industrial AI
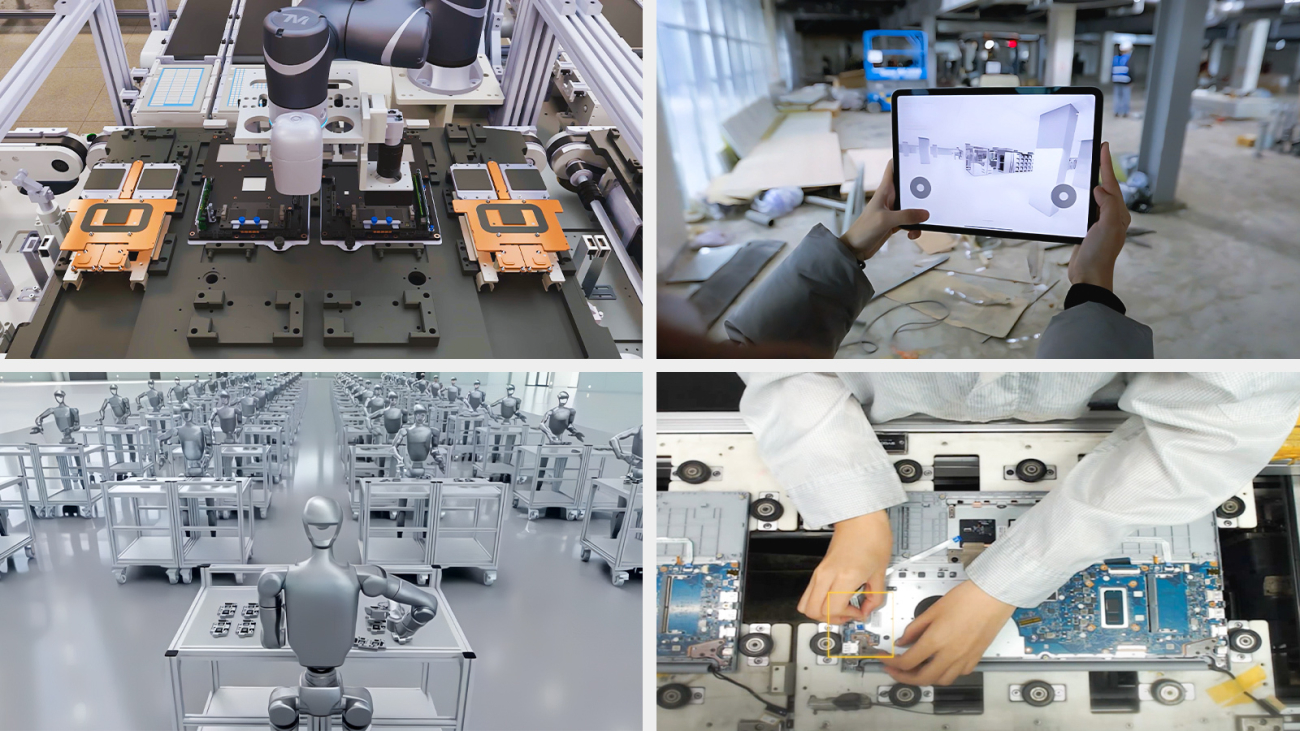
NVIDIA and Taiwan’s manufacturing ecosystem, including Delta Electronics, Foxconn, TSMC and Wistron, are showcasing this week at COMPUTEX in Taipei the crucial role digital twins play in accelerating industrial AI.
These electronics, semiconductor and robotics manufacturing leaders are using Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD) and NVIDIA Omniverse libraries and blueprints to develop physically based digital twins. This is transforming factory planning by unlocking new operational efficiencies and accelerating the development, testing and validation of autonomous robots and robotic fleets.
Many of these manufacturers are also extending the digitalization of their factories to the real world, using the NVIDIA AI Blueprint for video search and summarization (VSS) — now generally available and part of the NVIDIA Metropolis platform — to deploy video analytics AI agents into their operations and drive additional automation and optimizations in defect detection and other operations.
Taiwan Manufacturers Optimize Planning and Operations With Simulation and AI Agents
Taiwan’s leading electronics and semiconductor manufacturers are using digital twins, physically based simulation and AI agents to optimize existing operations and vastly accelerate the planning and commissioning of new factories.
Foxconn is leading the way. At its Taiwan facilities, Foxconn engineers rely on the Fii Digital Twin platform, developed with OpenUSD, Siemens and Omniverse technologies, to design and simulate robot work cells, assembly lines and entire factory layouts.
These digital twins connect to material control systems and use Autodesk Flexsim, NVIDIA cuOpt and NVIDIA Isaac Sim to enable engineers to simulate and dynamically optimize the flow of materials, equipment, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), automated guided vehicles, and other robots and humans. By developing a standard digital twin model for their factories, Foxconn can quickly migrate and easily reconfigure its designs and plans for new factory deployments.
Foxconn is using the NVIDIA Isaac GR00T N1 model, the NVIDIA Isaac GR00T-Mimic blueprint for synthetic manipulation motion generation and NVIDIA Isaac Lab to train industrial manipulator arms and humanoid robots for performing complex tasks such as screw-tightening, pick and place, assembly and cable insertion. Foxconn robotics developers use the Mega NVIDIA Omniverse Blueprint to simulate and test large robotic fleets comprising AMRs, manipulators and humanoid robots before deploying them in facilities.
To accelerate analysis and decision-making, Foxconn engineers use their digital twin platform to conduct thermal assessments of POD rooms across different scenarios. By connecting their digital twins to the Cadence Reality Digital Twin Platform and integrating NVIDIA PhysicsNeMo frameworks, teams can conduct thermal simulations 150x faster, reduce thermal risks and identify energy-saving opportunities.
Using the Omniverse Blueprint for AI factory digital twins, Foxconn can simulate and test GB200 Grace Blackwell Superchips in liquid-cooled PODs to replicate the conditions of an AI factory.
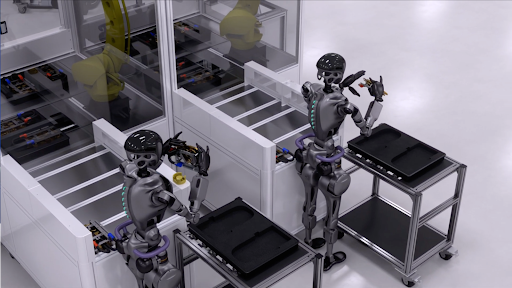
The company is also deploying video analytics AI agents using the VSS blueprint from NVIDIA Metropolis for real-time video analysis and insights in live production scenarios.
TSMC is collaborating with an AI-powered digital twins startup to optimize the planning and construction of its new fabs. TSMC taps into an AI engine and applications built with Omniverse libraries to transform traditional 2D computer-aided designs into rich, interactive 3D layouts of their complex facilities, including specialized areas like clean rooms.

Visualizing these optimized layouts in a digital twin allows planning teams to proactively identify and resolve equipment collisions, understand system interdependencies, and assess impacts on space and operational key performance indicators.
This AI-driven approach is enhanced by NVIDIA cuOpt for optimization and reinforcement learning with NVIDIA Isaac Lab, enabling the generation of intricate, multilevel piping systems in seconds — a task that traditionally requires substantial time and effort. This enables engineers to virtually validate complex pipe routing and drastically reduce design revisions, ultimately streamlining the entire fab development process.
TSMC also uses vision language models and vision foundation models to improve automated defect classification workflows — boosting efficiency to classify wafer product defects for engineers to pinpoint potential root causes for the issues. Beyond the use of digital twins and vision AI, TSMC also taps into NVIDIA CUDA-X software libraries and NVIDIA GPUs to accelerate its entire semiconductor chip design workflow — from lithography with NVIDIA cuLitho to semiconductor process simulation.
Wistron teams drive operational efficiencies, optimize layout planning of their plants, and train robots and workers with the Wistron Digital Twin (WiDT) platform. The platform is powered by software from Autodesk, Cadence and Microsoft and taps into NVIDIA AI and Omniverse libraries.
By connecting the WiDT platform to generative AI tools and real-time data from surface mount technology machines and shopfloor control systems, operations teams can visualize real-time dashboards to quickly diagnose and improve machine and plant performance.
Wistron robotics developers use the platform, and its integration with NVIDIA Isaac Sim, to simulate and test robotic arms. With a simulation-first approach, teams reduced the time needed for each arm to assemble parts on the production line by 12 seconds.

The Wistron digital twin platform also uses the VSS blueprint to create and curate training videos for teaching workers how to perform and manage complex tasks and scenarios. The platform uses NVIDIA Cosmos Tokenizer to help teams analyze and break down worker actions on the production line and improve standard operating procedures. This approach is enabling Wistron to accelerate onboarding, improve worker productivity and ensure safety.
Wiwynn uses AI-enabled digital twins built with Omniverse technologies to optimize factory layouts, simulate production, integrate cobots and enhance quality control through improved inspection and analysis. These solutions have driven significant manufacturing and logistics innovation and efficiencies.
Pegatron’s PEGAVERSE and PEGAAi platforms equip engineers and factory managers with digital twins that support many use cases, including factory planning, predictive maintenance, process optimization, resource planning, remote monitoring and quality control.
Teams also use the platforms to build visual AI agents to help workers perfect complex assembly tasks. These AI agents, developed with the NVIDIA AI Blueprint for VSS and NVIDIA Metropolis, have enabled Pegatron to augment assembly processes, reduce labor costs by 7% and decrease assembly line defect rates by 67%.
Kenmec and MetAI are using Omniverse technologies and the Mega NVIDIA Omniverse Blueprint to build physically accurate digital twins for simulating, testing and deploying warehouse automation solutions. Together, the teams virtualized the entire Chief Smart Logistics Center, creating a full-fidelity simulation environment that brings together physical dynamics, real-time controller logic, AI-driven testing and optimization — all within a simulated environment.
GIGABYTE operations teams are using digital twins developed with Omniverse libraries and connected to live IoT data from the manufacturing floor to improve operational monitoring of production systems. By visually flagging anomalies, including equipment issues and delays, the digital twins help teams quickly identify issues, conduct root cause analysis and take corrective actions.
Quanta Cloud Technology engineering, operations and logistics teams collaborate using digital twin solutions built with Omniverse to accelerate factory planning. Digital twins provide these cross-functional teams with access to the latest design data, enabling them to provide immediate feedback on proposed layouts, which leads to optimized workflows and improved space utilization. Teams can further extend collaboration sessions to external customers and suppliers so they can remotely contribute to design reviews and validation.

Manufacturers Embrace Digital Twins to Accelerate Robotics Development
In addition to creating the future in manufacturing, Taiwan manufacturers are using digital twins, powered by Omniverse libraries and blueprints, to develop the next wave of AI-enabled robots.
Delta Electronics is using Isaac Sim to optimize electronic component production and to simulate, train and validate its entire range of industrial robots — from AMRs to industrial manipulators.
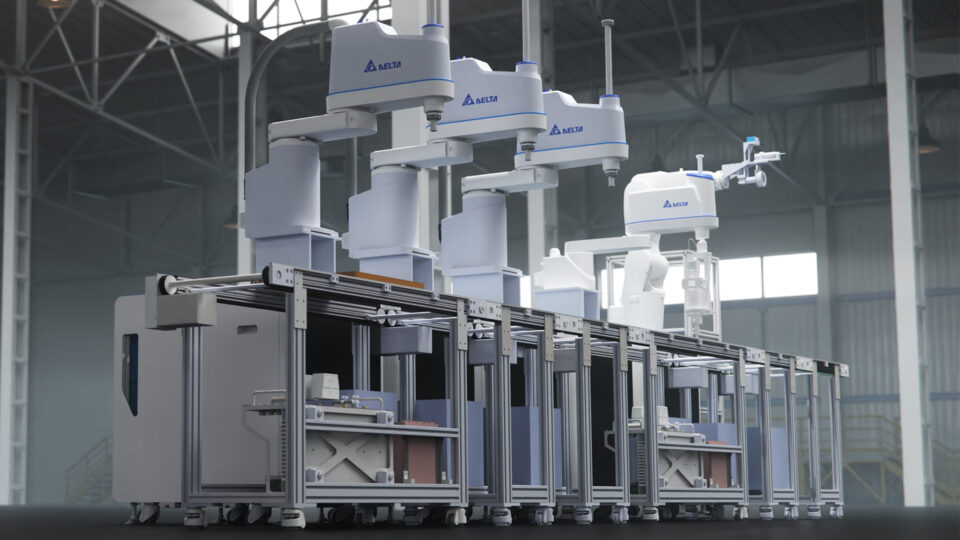

The company is transforming its expertise into a service by designing a cyber-physical integrated classroom to be launched soon in Taiwan, where customers learn to use the DIATwin platform to simulate and integrate Delta’s industrial equipment and robots to ensure a more effective implementation into their own production lines.
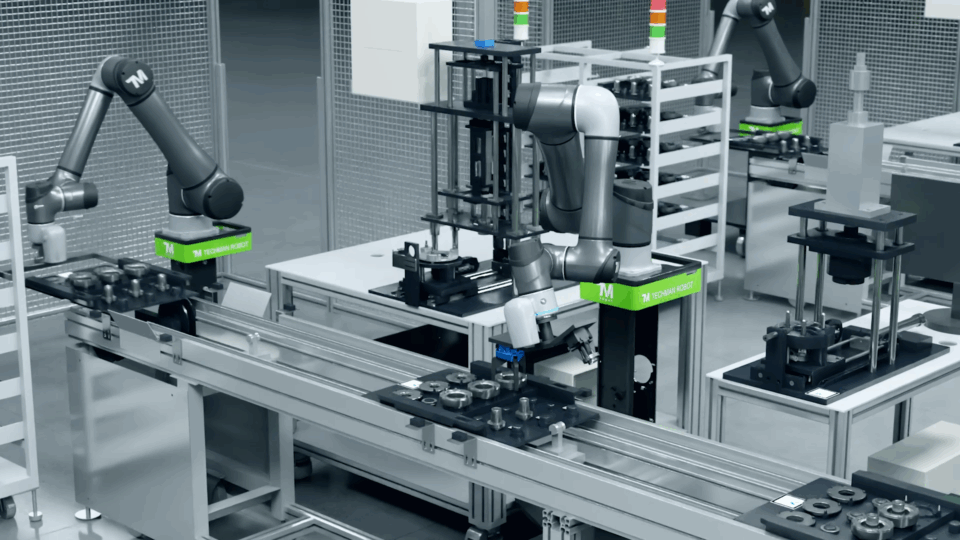
Techman Robot is advancing intelligent automation at Volkswagen’s Transparent Factory. Using Isaac Sim, Techman’s AI Cobots learn to operate on GESSbot AMRs in physically accurate simulations to perform real-time assembly, inspection and adaptive manipulation tasks with precision. By simulating robot behavior and workflows virtually, Techman Robot has reduced the time to program robots by 70% and improved robot productivity by 20%.
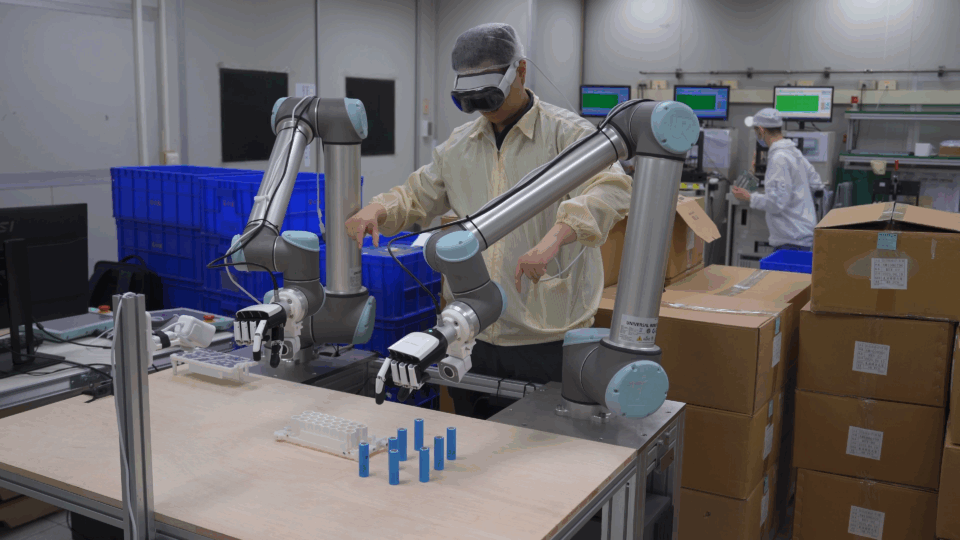

Foxlink is using the Isaac GR00T N1 model to add generalized intelligence and autonomy to its industrial robots used in manufacturing facilities.
Solomon’s AI vision solution, powered by NVIDIA Isaac Manipulator CUDA-X acceleration libraries, is helping Inventec significantly accelerate its robotic server inspection process by boosting complex motion planning speed by up to 8x and reducing errors by 50%.
Kudan is integrating its Visual SLAM technology with Isaac Perceptor CUDA-X acceleration libraries into NexAIoT’s AMR, NexMOV-2. This integration uses advanced 3D perception and navigation, enabling them to navigate complex, unstructured environments such as manufacturing, logistics and healthcare facilities with greater precision and reliability.
MSI is powering its industrial robots with the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin module to perform a variety of tasks, from pick-and-place and material handling to delivering payloads inside large warehouses and facilities.

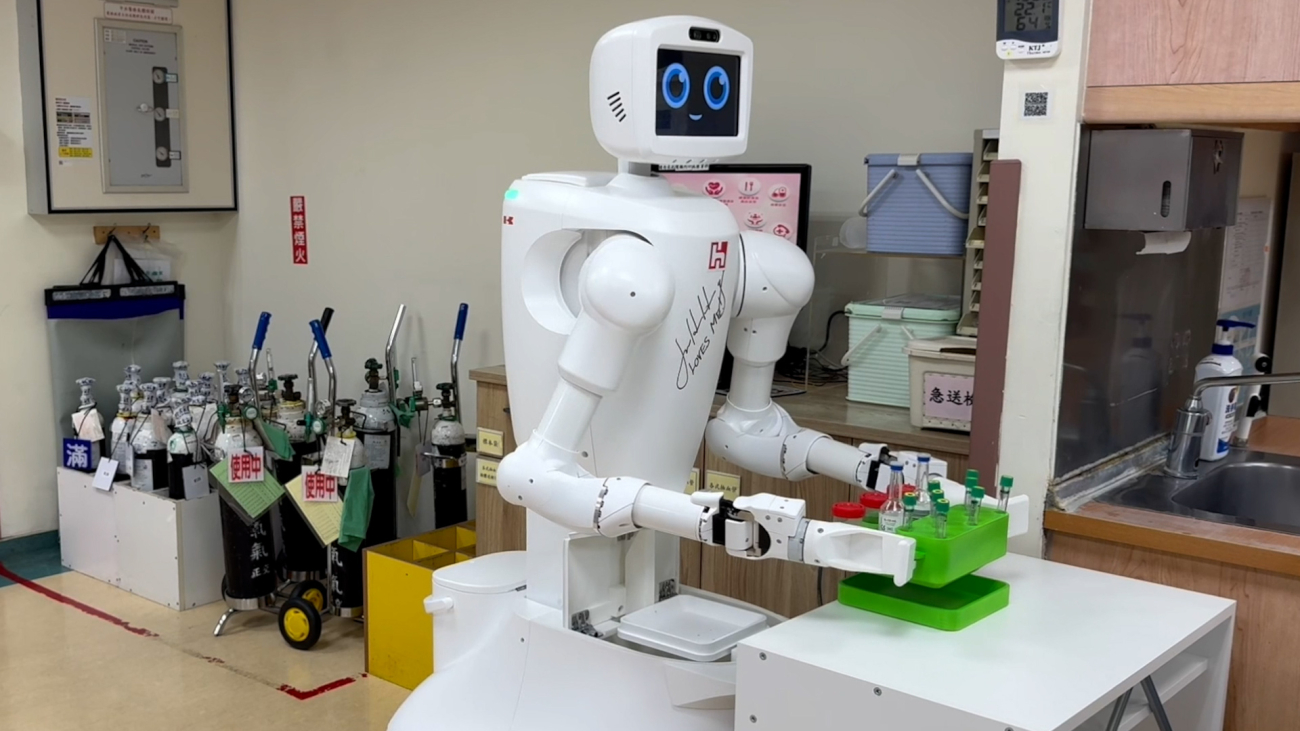
In healthcare, Adata and Advantech are jointly using Isaac Sim, Isaac Perceptor and Jetson Orin to develop AMRs for disinfecting hospitals. This collaboration has reduced deployment time by 70% and made the disinfection process 3x faster. Ubitus is also using the Isaac platform to train G1 humanoid robots to deliver medical checkup materials and specimens, helping alleviate labor shortages in hospitals.
Learn more by watching the COMPUTEX keynote from NVIDIA founder and CEO Jensen Huang and attending sessions at NVIDIA GTC Taipei, running through May 22.
See notice regarding software product information.
Featured image courtesy of Quanta (top left), Wistron (top right), Foxconn (bottom left), Pegatron (bottom right).
Talk to Me: NVIDIA and Partners Boost People Skills and Business Smarts for AI Agents
Call it the ultimate proving ground. Collaborating with teammates in the modern workplace requires fast, fluid thinking. Providing insights quickly, while juggling webcams and office messaging channels, is a startlingly good test, and enterprise AI is about to pass it — just in time to provide assistance to busy knowledge workers.
To support enterprises in boosting productivity with AI teammates, NVIDIA today introduced a new NVIDIA Enterprise AI Factory validated design at COMPUTEX. IT teams deploying and scaling AI agents can use the design to build accelerated infrastructure and easily integrate with platforms and tools from NVIDIA software partners.
NVIDIA also unveiled new NVIDIA AI Blueprints to aid developers building smart AI teammates. Using the new blueprints, developers can enhance employee productivity through adaptive avatars that understand natural communication and have direct access to enterprise data.
Blueprints for Engaging, Insightful AI Agents
Enterprises can use NVIDIA’s latest AI Blueprints to create agents that align with their business objectives. Using the Tokkio NVIDIA AI Blueprint, developers can create interactive digital humans that can respond to emotional and contextual cues, while the AI-Q blueprint enables queries of many data sources to infuse AI agents with the company’s knowledge and gives them intelligent reasoning capabilities.
Building these intelligent AI agents is a full-stack challenge. These blueprints are designed to run on NVIDIA’s accelerated computing infrastructure — including data centers built with the universal NVIDIA RTX PRO 6000 Server Edition GPU, which is part of NVIDIA’s vision for AI factories as complete systems for creating and putting AI to work.
The Tokkio blueprint simplifies building interactive AI agent avatars for more natural and humanlike interactions.
These AI agents are designed for intelligence. They integrate with foundational blueprints including the AI-Q NVIDIA Blueprint, part of the NVIDIA AI Data Platform, which uses retrieval-augmented generation and NVIDIA NeMo Retriever microservices to access enterprise data.
AI Agents Boost People’s Productivity
Customers around the world are already using these AI agent solutions.
At the COACH Play store on Cat Street in Harajuku, Tokyo, imma provides an interactive in-store experience and gives personalized styling advice through natural, real-time conversation.
Marking COACH’s debut in digital humans and AI-driven retail, the initiative merges cutting-edge technology with fashion to create an immersive and engaging customer journey. Developed by Aww Inc. and powered by NVIDIA ACE, the underlying technology that makes up the Tokkio blueprint, imma delivers lifelike interactions and tailored style suggestions.
The experience allows for dynamic, unscripted conversations designed to connect with visitors on a personal level, highlighting COACH’s core values of courage and self-expression.
“Through this groundbreaking innovation in the fashion retail space, customers can now engage in real-time, free-flowing conversations with our iconic virtual human, imma — an AI-powered stylist — right inside the store in the heart of Harajuku,” said Yumi An King, executive director of Aww Inc. “It’s been inspiring to see visitors enjoy personalized styling advice and build a sense of connection through natural conversation. We’re excited to bring this vision to life with NVIDIA and continue redefining what’s possible at the intersection of AI and fashion.”
Watch how Aww Inc. is leveraging the latest Tokkio NVIDIA AI Blueprint in its AI-powered virtual human stylist, imma, to connect with shoppers through natural conversation and provide personalized styling advice.
Royal Bank of Canada developed Jessica, an AI agent avatar that assists employees in handling reports of fraud. With Jessica’s help, bank employees can access the most up-to-date information so they can handle fraud reports faster and more accurately, enhancing client service.
Ubitus and the Mackay Memorial Hospital, located in Taipei, are teaming up to make hospital visits easier and friendlier with the help of AI-powered digital humans. These lifelike avatars are created using advanced 8K facial scanning and brought to life by Ubitus’ AI model integrated with NVIDIA ACE technologies, including NVIDIA Audio2Face 3D for expressions and NVIDIA Riva for speech.
Deployed on interactive touchscreens, these digital humans offer hospital navigation, health education and registration support — reducing the burden on frontline staff. They also provide emotional support in pediatric care, aimed at reducing anxiety during wait times.
Ubitus and the Mackay Memorial Hospital are making hospital visits easier and friendlier with the help of NVIDIA AI-powered digital humans.
Cincinnati Children’s Hospital is exploring the potential of digital avatar technology to enhance the pediatric patient experience. As part of its ongoing innovation efforts, the hospital is evaluating platforms such as NVIDIA’s Digital Human Blueprint to inform the early design of “Care Companions” — interactive, friendly avatars that could help young patients better understand their healthcare journey.
“Children can have a lot of questions about their experiences in the hospital, and often respond more to a friendly avatar, like stylized humanoids, animals or robots, that speaks at their level of understanding,” said Dr. Ryan Moore, chief of emerging technologies at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital. “Through our Care Companions built with NVIDIA AI, gamified learning, voice interaction and familiar digital experiences, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital aims to improve understanding, reduce anxiety and support lifelong health for young patients.”
This early-stage exploration is part of the hospital’s broader initiative to evaluate new and emerging technologies that could one day enhance child-centered care.
Software Platforms Support Agents on AI Factory Infrastructure
AI agents are one of the many workloads driving enterprises to reimagine their data centers as AI factories built for modern applications. Using the new NVIDIA Enterprise AI Factory validated design, enterprises can build data centers that provide universal acceleration for agentic AI, as well as design, engineering and business operations.
The Enterprise AI Factory validated design features support for software tools and platforms from NVIDIA partners, making it easier to build and run generative and agent-based AI applications.
Developers deploying AI agents on their AI factory infrastructure can tap into partner platforms such as Dataiku, DataRobot, Dynatrace and JFrog to build, orchestrate, operationalize and scale AI workflows. The validated design supports frameworks from CrewAI, as well as vector databases from DataStax and Elastic, to help agents store, search and retrieve data.
With tools from partners including Arize AI, Galileo, SuperAnnotate, Unstructured and Weights & Biases, developers can conduct data labeling, synthetic data generation, model evaluation and experiment tracking. Orchestration and deployment partners including Canonical, Nutanix and Red Hat support seamless scaling and management of AI agent workloads across complex enterprise environments. Enterprises can secure their AI factories with software from safety and security partners including ActiveFence, CrowdStrike, Fiddler, Securiti and Trend Micro.
The NVIDIA Enterprise AI Factory validated design and latest AI Blueprints empower businesses to build smart, adaptable AI agents that enhance productivity, foster collaboration and keep pace with the demands of the modern workplace.
See notice regarding software product information.